If you ask them, most teachers are very happy, occasionally, to replace their usual mask with the one of an eager student. I don’t often get to participate in writing workshops as a consumer, but when I do it’s always fascinating. For the last one I took part in, I chose it because of its intriguing promise to use Shakespeare’s work as its starting point. Last weekend I was drawn to Amy E. Weldon’s workshop at Keats House which promised to do the same with Keats’ work.

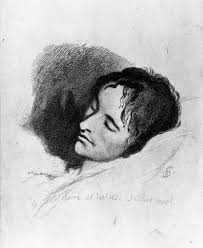
This event was part of Keats House’s bicentenary celebrations and a dozen of us gathered in the atmospheric Chester Room on a sunny day (Keats gazing down at us from Joseph Severn’s painting on the wall). Amy Weldon – a Professor of English at Luther College, USA, whose book on creative writing has recently been published by Bloomsbury – was very good at reminding us of the presence of ‘Brother John’ in the surrounding fabric of the house and its beautiful gardens, where he wrote his ‘Ode to a Nightingale’. Probably no-one there – teachers, journalists, writers of poetry and teen fiction, autodidacts – really needed it, but she also kicked off with an enthusiastic reminder of the importance of “books and ideas”. And it was a number of Keats’ own ideas – as expressed in his letters – that we discussed first of all.

I’ve written elsewhere on this blog about the importance of Keats’ ideas for my own work and it powerfully struck me again, joining Amy and the other workshoppers in considering them, how coherent they are, despite being expressed and developed in scrawled letter form over a period of 2 or 3 years. From his ‘taking part’ in the sparrow’s existence, or that of the stoat or field-mouse, to the belief that poetry ought not to startle or amaze with itself (but with its subject), to his understanding that “extensive knowledge” is what gives a writer the kind of shoulders that are sufficiently “fledged” to enable creative flight, to his brilliant, improvised description of the gathering of such knowledge in the letter written in Spring 1819. The latter is the vale of soul-making letter to his brother George in which our identity (Keats’ word is ‘Soul’) is accumulated/created through the heart’s emotional encounters with the world. Without such encounters – the sparrow, the stoat and field-mouse, and this is what he means by extensive knowledge, we must extend ourselves in such encounters with the Other – we are not able to suck an Identity from experience and – like children who die tragically young – we have had “no time to learn of, and be altered by, the heart”.
Such encounters – vigorously and passionately advocated by the workshop leader – formed the basis for the creative side of the rest of the day. We were sent outside to roam around the garden in search of sensory images, in particular, the May-time flowers in their blooming colours and scents, the birdsong, the noise of traffic or quiet conversations of other visitors, the smooth or veined surface of leaves, the rough gravel paths. On the day, I didn’t taste anything myself – perhaps others successfully used all five senses! We jotted as if our lives depended on it – the task made easier by Amy’s insistence on the messiness of writers’ notebooks, on the provisional nature of whatever it was we were writing.

Amy’s approach on this occasion was to direct us towards fairly openly/widely-defined tasks – as in this first one – rather than setting out a framework within which to work. Such frameworks might be formal or linguistic (repetitions, the use of particular words and so on) or models derived from other writers and can often lead workshop participants towards experimenting, bumping us out of our usual modes, forms and tones. Nevertheless, we all returned from the task with plenty of notes and – for those who attend such events – Amy’s suggestions as to next steps were familiar enough. Circle the “interesting” moments in what you have written down (interesting here is wholly self-defined). Find and remove editorial (directive) words like ‘beautiful’. These latter tend to be adjectives and adverbs and, if not removed, they were to be replaced with more directly sensory words – so not ‘beautiful’ but ‘lime green’. Another suggestion – which I found very difficult to put into practice – was to remove all words of more than one syllable. But you can see the direction of travel here: the valuing of plainness and the directness of sensory experience over anything close to judgment or the writer looking to ‘persuade’ the reader.

During lunchtime – apart from feeding and drinking – our tasks were to make a list of ten things we “noticed” and to actually make an attempt to draw one thing. In each case – Amy was always clear on this – anything was to be grist for the mill, so we had to resist bringing in censorship or evaluation: two people wearing identical hats; the type of cakes on sale down the road; overheard comments from passers-by; what they were promoting at Keats Pharmacy near the station. I drew a house on Devonshire Hill. Very badly.
Once we’d gathered again, Amy quoted John Ruskin on the value of drawing, I think to the effect that even writers ought to try to draw as in doing so they begin to see more “brutally” or clearly. I can’t find the actual quote itself but, having drawn my house on Devonshire Hill, I can testify that he’s right. It makes you look first – language comes second. However dismal the results, I’ll try drawing again. We also shared some of our ten observations – though interestingly neither the observations nor the drawings were developed any further on this occasion.

Instead we read an extract from Amy’s book, The Writer’s Eye. The extract suggested that an ‘image’ is a mental picture (probably from the past) that releases emotions into your mind in the same way as a bunch of mint leaves from a garden releases flavour and colour when steeped in water (good image). These sorts of mental images can be starting points for poems or stories – much more so than (the common colloquialism of) starting with an ‘idea’. The latter tend to be dead, whereas the ‘image’ is by definition enlivened with emotions. So our next task was to find such an image in ourselves and to write on it (again our instructions were open as opposed to delimited or framed). Later we had the chance to re-cast what we had written – perhaps re-starting from ‘interesting’ things we had again circled ourselves.
There had so far been no reading round of anything we’d written (apart from some of the 10 things observed over lunchtime). Eventually, we were put into pairs to give some feedback on the final piece written, now read aloud. Amy’s instructions here were interesting. The listener was only to offer two types of comment. The more positive one was in the form of ‘More like this’. And to express reservations, rather than ‘I don’t like this’ or ‘I don’t get this’, we were to say simply, ‘This stops me’. I thought both these formulations worked well and I would use them again.

It was a good day and I’m sure we all came away with several pages of material to work on. One of Amy’s stories stuck in my mind and, though about a prose writer, is applicable to poetry too. A friend of hers goes to a burger joint. Over the grill, with his back to the customers, the owner is flipping burgers, not looking round. The friend gives his order. Still the guy goes on flipping burgers, not looking round, not responding. After a moment or two, the friend orders again, verbatim, just to be clear what he wants, perhaps just a little louder. Still without turning round, the owner says simply: ‘Yuh said that already’. The writer friend, I presume, did get his burger, but he also came away with the guy’s phrase as a memorable maxim for those of us who write, then out of our anxiety to communicate, to be understood, write it again: ‘Yuh said that already’. Time to pick up your editing pen . . .


 Earth continues by diagnosing the state of slavery into which England has fallen. This – and the following passage with its more positive analysis of what Freedom means to working people – makes for powerful, relevant, realistic reading in contrast to Shelley’s hard-to-pin-down mechanisms of political change. Slavery is to have to work and be paid only enough to live for another day’s work. It is to work not for oneself but for “tyrants”. It is to see family suffering and dying, to go hungry while the rich man surfeits his dogs. It is to suffer the “forgery” of paper money, to have no control over one’s own destiny. It is – when driven to the point of protest – a more direct reference to events in Manchester – “to see the Tyrant’s crew / Ride over your wives and you”.
Earth continues by diagnosing the state of slavery into which England has fallen. This – and the following passage with its more positive analysis of what Freedom means to working people – makes for powerful, relevant, realistic reading in contrast to Shelley’s hard-to-pin-down mechanisms of political change. Slavery is to have to work and be paid only enough to live for another day’s work. It is to work not for oneself but for “tyrants”. It is to see family suffering and dying, to go hungry while the rich man surfeits his dogs. It is to suffer the “forgery” of paper money, to have no control over one’s own destiny. It is – when driven to the point of protest – a more direct reference to events in Manchester – “to see the Tyrant’s crew / Ride over your wives and you”.


 The third reason Shelley gives – via the voice of the earth – also offers only equivocal, indeed very uncomfortable, hope. Offering little or no consolation to the victims and their relations – though a point proven true through many centuries – such massacres by repressive forces will prove an inspiration to those who come after them: “that slaughter to the Nation / Shall steam up like inspiration”. Using another of his images for revolutionary fervour, this steam will eventually result in a volcanic explosion, “heard afar”. Once more in this poem, these reverberations are translated into words to mark “Oppression’s thundered doom”, stirring the people in their on-going fight for justice and liberty. Shelley concludes with the actual words he imagines being uttered – and we have heard them before:
The third reason Shelley gives – via the voice of the earth – also offers only equivocal, indeed very uncomfortable, hope. Offering little or no consolation to the victims and their relations – though a point proven true through many centuries – such massacres by repressive forces will prove an inspiration to those who come after them: “that slaughter to the Nation / Shall steam up like inspiration”. Using another of his images for revolutionary fervour, this steam will eventually result in a volcanic explosion, “heard afar”. Once more in this poem, these reverberations are translated into words to mark “Oppression’s thundered doom”, stirring the people in their on-going fight for justice and liberty. Shelley concludes with the actual words he imagines being uttered – and we have heard them before:


 But as Shelley’s sentence crosses the next stanza break – ie. without any clear pause – the seemingly unstoppable parade of bloodshed, inequality, injustice and hypocrisy is strangely interrupted by a counter personification. A crazed-looking young woman (“a maniac maid”) runs out declaring that her name is Hope, though the narrator says “she looked more like Despair”. The perception here is interesting as even Shelley’s narrator has been so infected by the toxic atmosphere spread by Anarchy that the girl (who is soon to bring about a challenge to Anarchy) looks to be insane and more resembles the absence of hope than otherwise. This is one of Shelley’s core political beliefs and had already appeared in the closing lines of Prometheus Unbound. There, Demogorgon urges optimism in the long term conflict with abusive power: “to hope, till Hope creates / From its own wreck the thing it contemplates”. The movement for Reform will – it seems – have to come close to despair, or its own wreck, before the powers of Anarchy are likely to be defeated.
But as Shelley’s sentence crosses the next stanza break – ie. without any clear pause – the seemingly unstoppable parade of bloodshed, inequality, injustice and hypocrisy is strangely interrupted by a counter personification. A crazed-looking young woman (“a maniac maid”) runs out declaring that her name is Hope, though the narrator says “she looked more like Despair”. The perception here is interesting as even Shelley’s narrator has been so infected by the toxic atmosphere spread by Anarchy that the girl (who is soon to bring about a challenge to Anarchy) looks to be insane and more resembles the absence of hope than otherwise. This is one of Shelley’s core political beliefs and had already appeared in the closing lines of Prometheus Unbound. There, Demogorgon urges optimism in the long term conflict with abusive power: “to hope, till Hope creates / From its own wreck the thing it contemplates”. The movement for Reform will – it seems – have to come close to despair, or its own wreck, before the powers of Anarchy are likely to be defeated. This mist – later called a “Shape” – is one of the mysteries of the poem’s politics. Hope provokes its appearance. At first weak, it gathers in strength. Shelley compares it to clouds that gather “Like tower-crowned giants striding fast, / And glare with lightnings as they fly, /And speak in thunder to the sky”. In the next few stanzas it becomes more soldierly, “arrayed in mail”, compared to the scales of a snake (for Shelley the snake was usually an image of just rebellion not of evil), yet it is also winged. It wears a helmet with the image of the planet Venus on it. It moves softly and swiftly – a sensed but almost unseen presence. And rather than any military action or campaign of civil disobedience, this Shape, conjured by Hope, creates thinking:
This mist – later called a “Shape” – is one of the mysteries of the poem’s politics. Hope provokes its appearance. At first weak, it gathers in strength. Shelley compares it to clouds that gather “Like tower-crowned giants striding fast, / And glare with lightnings as they fly, /And speak in thunder to the sky”. In the next few stanzas it becomes more soldierly, “arrayed in mail”, compared to the scales of a snake (for Shelley the snake was usually an image of just rebellion not of evil), yet it is also winged. It wears a helmet with the image of the planet Venus on it. It moves softly and swiftly – a sensed but almost unseen presence. And rather than any military action or campaign of civil disobedience, this Shape, conjured by Hope, creates thinking: Yet in the calm aftermath of these events, there comes a sense of renovation, a “sense awakening and yet tender / Was heard and felt” and, most importantly, there are further words. This time the speaker is unclear though it is “As if” the earth itself, the mother of English men and women, feeling such bloodshed on her brow, translates this spilt blood into a powerful, irresistible language, “an accent unwithstood”. Shelley repeats “As if” once more, confirming the mystery of this voice, a voice which proceeds now to speak the whole of the remainder of the poem. For Shelley, Poetry in his broad sense is “vitally metaphorical” and the earth’s imagined speeches convey a sense that the cause of liberty is in accordance with the truly understood (surely Rousseauistic) nature of creation.
Yet in the calm aftermath of these events, there comes a sense of renovation, a “sense awakening and yet tender / Was heard and felt” and, most importantly, there are further words. This time the speaker is unclear though it is “As if” the earth itself, the mother of English men and women, feeling such bloodshed on her brow, translates this spilt blood into a powerful, irresistible language, “an accent unwithstood”. Shelley repeats “As if” once more, confirming the mystery of this voice, a voice which proceeds now to speak the whole of the remainder of the poem. For Shelley, Poetry in his broad sense is “vitally metaphorical” and the earth’s imagined speeches convey a sense that the cause of liberty is in accordance with the truly understood (surely Rousseauistic) nature of creation.
 Waiblinger was a real Holderlin fan. The older poet’s novel, Hyperion, had appeared in 1822
Waiblinger was a real Holderlin fan. The older poet’s novel, Hyperion, had appeared in 1822 




![moulin-glacier-11[2]](https://martyncrucefix.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/moulin-glacier-112.jpg?w=352&h=264)