A few weeks back, I was asked to contribute to an afternoon event in Palmers Green Library, north London, with the title – from Robert Frost’s poem – ‘The Road Not Taken’. It was introduced by Maggie Butt, with readings of their own poetry around the theme by Mark Holihan and Denise Saul. I was also asked to deliver a few thoughts on the work of Robert Frost. What follows is an edited transcript of what I said then and I think of it as a basic introduction for the general reader to Frost’s work and some of the ideas which I see recurring in it. As previous posts have mentioned, I’ve been teaching Frost for a few years recently – thanks to all those students who made me go back and read the poems again!

Despite the apparent simplicity of many of his poems, the real identity of Robert Frost (1874-1963) is hard to pin down. Though raised in late 19th century America, his first book was published in England. Though on the brink of the Modern, a year before the First World War, these poems used plain language and traditional forms. He loved Europe, befriending Edward Thomas – stirring him from prose into poetry – yet Frost sailed back to the US, to farming, north of Boston. By all accounts he was never a very successful farmer, though he often presented himself as talking downright farmer-like common sense. Some find his work consolatory; but he was famously called a ‘terrifying’ poet, a bleak Modernist.
If all this sounds slippery, then Frost took it into his poetics too. He said that, while writing a poem, he was conscious of saying two things at once. But he always wanted to say the first thing so well that any reader who liked that part of the poem might feel able to rest there. Yet, he implies, for those interested in going further, beyond the particular, overt or explicit meaning – say, two farmers re-building a wall between their properties, a man stopping to watch snow fall in a wood, a mower and a butterfly – there is always an ulterior meaning (at least one) that might also be opened up.
At all levels, such defining walls, barriers and boundaries – physical, mental, spiritual – proliferate in Frost’s work. But his view of them is complex. These walls are often porous. But sometimes they can seem impenetrable. I can’t vouch for the accuracy of his biological knowledge, but here is something else Frost repeatedly jotted down in his Notebooks: “All life is cellular. No living particle of matter however small has yet been found without a skin – without a wall.”
On one side, these secure boundaries seem necessary for a successful life – like the wall round all cellular organisms. He would say: “I want to be a person. And I want you to be a person”. But the dangers are obvious. The cellular wall of identity becomes more than a means of self-definition and grows to become an exclusion zone, a solitary place, a state of solipsism. Many of Frost’s figures and narrators are found to be struggling with this state. Yet Frost’s comments about identity, wanting to be a person, wanting you to be a person, in fact continue: “then we can be as interpersonal as you please. We can pull each other’s noses – do all sorts of things”.
So the presence of these cellular walls do not necessarily hold us back. They are as often porous or permeable. Yet they seem also to offer a firm foundation from which we may reach out, we can humanly interact. We can pull each other’s noses. And there is indeed much pulling of noses in Frost’s poems. In particular, he liked to pull the nose of the person he chose to narrate many of his poems. There is very often an irony at work against the speaker. His poems are often more dramatic than lyric.
We might ask why is Frost so concerned about being a person, about the relative security of identity? Because, in other moods, he knows the dangers posed by the absence of any functioning cellular membrane: the leaking out of personality into the surrounding world, of identity dissipating to become nothing, the risk – as it were – of personal extinction.

There is a little poem called ‘The Cow in Apple Time’ which (on the face of it) is about a cow who is driven by an unspecified desire to disregard the walls about her pasture. The wall is no more than an open gate to her. She charges through and greedily eats fallen apples, growing intoxicated, her face splattered with apple juice. But in this kind of gluttonous state she grows sick, in pain:
She bellows on a knoll against the sky.
Her udder shrivels and the milk goes dry.
It’s a perfectly satisfying poem about a rural incident – perhaps Farmer Frost, had once witnessed it himself. But there is Frost’s ulteriority too. The cow is consistently described using terms which anthropomorphise her. The wall breaker is perhaps on one level really human, a rebel, a sinner – written in 1914, some have even suggested the cow is an invasive force. However we see her, she is punished for her disregard of, her undervaluing of, those walls and boundaries which perhaps ought to serve to define her life.
Remember this is the same Robert Frost who disparaged the writing of free verse, by many of his more obviously Modernist contemporaries, as trying to play tennis with the net down. The same Robert Frost who disparaged the, then fashionable, interest in Surrealism with its wild leaps over convention, its dislocation of the senses, the shock value of the illogical. For Frost such practices could lead only “to undirected associations and kicking ourselves from one chance suggestion to another in all directions as of a hot afternoon in the life of a grasshopper”.

The cow with the aching stomach is paralleled by a dying peach tree in ‘There Are Roughly Zones’. The narrator has moved “far north” and has transplanted a peach tree and now the northern winter is threatening it. He sits indoors and frets about it, trying to blame the weather rather than himself. But self-criticism arises all the same and it is human “ambition” that gets the blame, that “limitless trait in the hearts of men”. More precisely:
[. . .] though there is no fixed line between right and wrong,
There are roughly zones whose laws must be obeyed.
I love the messy pragmatism implied by “roughly zones”. One of his recurring concerns, Frost said, was with “the impossibility of drawing sharp lines and making exact distinctions” – no red lines, lines in the sand, defined boundaries, but zones of negotiation, places calling for compromise, no fundamental clarity, rather a feeling-out, a region requiring a dialogue.
As in a poem like ‘The Tuft of Flowers’. A man comes to a mown field to turn the cut grass, the hay, to help its drying. He looks about for the man who had earlier mowed the grass:
But he had gone his way, the grass all mown,
And I must be, as he had been, – alone,
‘As all must be,’ I said within my heart
The hermetically cellular, or as we would now say, atomised nature of society seems to be assumed by the narrator. It looks like there is going to be no breaking of boundaries here. But a “[be]wildered” butterfly passes him, looking for flowers that grew there yesterday, now cut down. The butterfly leads him to a “leaping tongue of bloom” left deliberately, out of “sheer morning gladness” by the mower. The narrator hears the message from this “tongue of bloom” which speaks of each man as a “spirit kindred” to the other. It’s as if they now enter into a dialogue, revising the earlier solipsistic observation. Now:
‘Men work together,’ I told him from the heart,
‘Whether they work together or apart.’
There is a rosy-edged hint of sentimentality here perhaps. But the fanciful dialogue between the two men (who actually never meet) represents a successful negotiation into that rough zone between individuals, the cellular membrane is actually permeable, and the result here is consolatory.
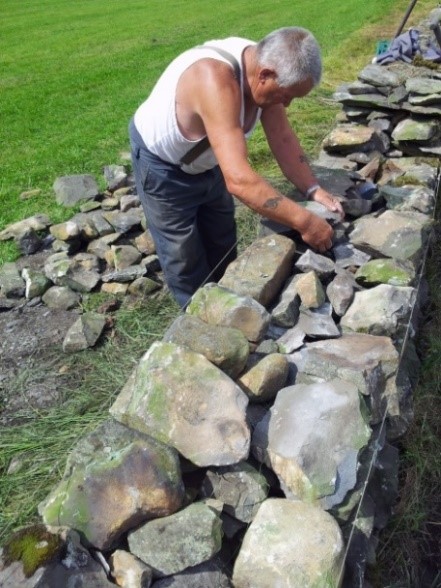

In ‘Mending Wall’, two farmers meet to patrol on either side of a dry-stone wall marking the boundary between their farms. Parts of it are always falling down. They build it back up. But the paradox is that the action of building up what separates them, brings them together each year to perform the task. The wall does not prevent or act as a brake on their relationship – rather it facilitates it – it perhaps is their relationship, what links them. From their respective sides – from their respective identities or persons – they are free to become ‘interpersonal’. But the mischievous, sceptical, modern-minded narrator expresses doubts about the importance of walls, particularly when “He is all pine and I am apple orchard”. His neighbour is a more traditional, unquestioning man, who likes to repeat his father’s advice: “Good fences make good neighbours”. The narrator mocks him (though in silence, in his head) as “an old-stone savage”, lost in actual and intellectual “darkness”. But it is significant that the wall-believer has the last word. For me, it is the moderniser is the one being ironised. If he was a versifier, he’d be trying to write poems with the net down.
Why Frost’s concern with the importance of walls? Because – in still other moods – he has looked into the abyss of experience without them. One example is given in the 16 terrifying lines of ‘Desert Places’. The narrator here seems to have taken the more modern, sceptical wall-mender’s view to heart. It seems there are no bounds here – all have vanished under “Snow falling and night falling fast oh fast”. That note of fear there adds to the nightmare feeling and when the outward-looking eye turns to look within – to find himself – he finds nothing: “I am too absent-spirited to count”. That phrase is an echo of ‘absent-minded’. There is a vacancy within and without – no mind, spirit, self, identity. There is only the concluding, devastating rhymes of “empty spaces . . . where no human race is . . . my own desert places”.
And if ‘Desert Places’ evokes the desolation of a world viewed in the absence of a relatively secure cell-walled self, then ‘The Most of It’ shows us the horrifying effects of being walled in. In this poem, the narrator “thought he kept the universe alone”. There seems nothing else but him, only a “mocking echo of his own [voice]”. Yet he does remotely feel a desire for dialogue – perhaps just in being human – and does express a desire not for “copy speech. / But counter-love, original response”. But when the universe does eventually break into his consciousness, it arrives not in the form of dialogue or a negotiated relationship but as an utterly alien thing.
It emerges only as a strange, vague “embodiment” that “crashed” and “splashed” towards him and is recognised only by means of a simile. Perhaps it is an elk.
As a great buck it powerfully appeared,
Pushing the crumpled water up ahead,
And landed pouring like a waterfall,
And stumbled through the rocks with horny tread,
And forced the underbrush—and that was all.
There, Frost captures the egoist’s struggle to comprehend what is other than him; followed by the arrogance of his dismissal of it. And perhaps this is a particularly masculine thing. Yet there is no need to attribute these feelings to Frost himself. The speaker is best read as a dramatic representation of one extreme of Frost’s concern for borders and boundaries that are vital for our own selfhood yet must be porous enough to allow for knowledge and experience.
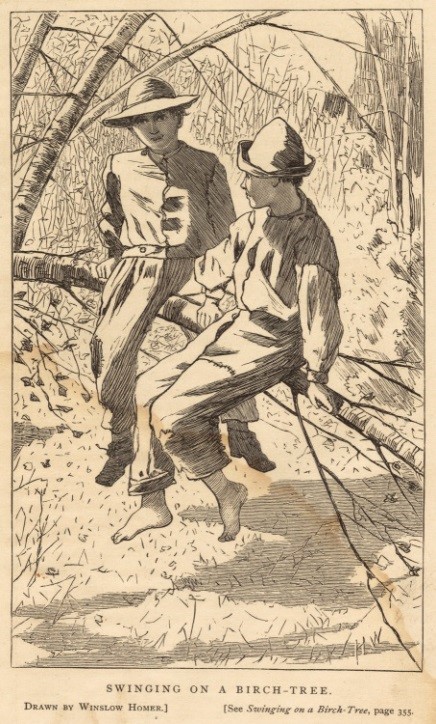

So in ‘Birches’ the narrator remembers – as a boy – climbing slender birch trees, to the top, only to leap out and bend them down with his weight. This swinging of birches can be seen – ulteriorly – as representing Frost’s belief in those negotiated rough zones of a life. We climb up, out of our element, but not too far:
It’s when I’m weary of considerations,
And life is too much like a pathless wood
Where your face burns and tickles with the cobwebs
Broken across it, and one eye is weeping
From a twig’s having lashed across it open.
I’d like to get away from earth awhile
And then come back to it and begin over.
May no fate wilfully misunderstand me
And half grant what I wish and snatch me away
Not to return. Earth’s the right place for love:
I don’t know where it’s likely to go better.
And if we find this frustratingly ambivalent – Frost sitting carefully on the fence – then he often rubs our noses in it. ‘Stopping by Woods on a Snowy Evening’ famously concludes with two lines which are identical. For me, the repetition introduces greater ambiguity into the moment. Does the narrator stop, perhaps to die, entranced by the snowfall? Or does he shake himself up, turn back to his life in the village, his roles and responsibilities?
Whose woods these are I think I know.
His house is in the village, though;
He will not see me stopping here
To watch his woods fill up with snow.
My little horse must think it queer
To stop without a farmhouse near
Between the woods and frozen lake
The darkest evening of the year.
He gives his harness bells a shake
To ask if there is some mistake.
The only other sound’s the sweep
Of easy wind and downy flake.
The woods are lovely, dark, and deep,
But I have promises to keep,
And miles to go before I sleep,
And miles to go before I sleep.
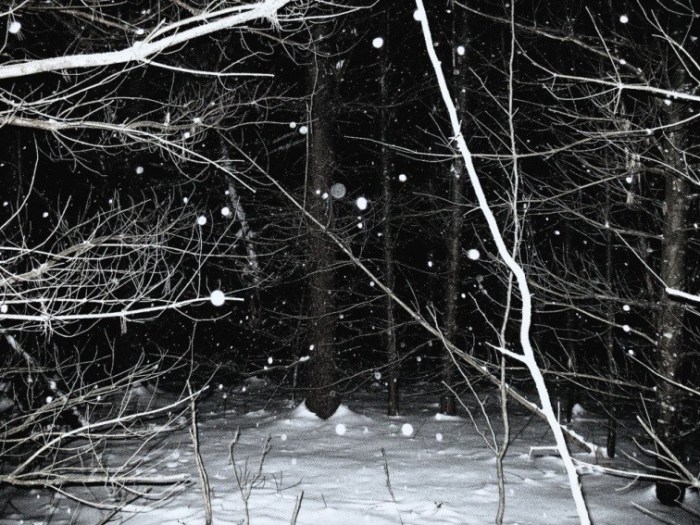

Frost throws the question back to the reader. What Frost knows is that we do not keep the universe alone. We are parts of a whole – but the borderlands are uncertain – sometimes we cross them and lose touch with ourselves, at other times we too easily accept them and fall into egotistical isolation. There maybe be a happy medium – but Frost’s dynamic poems suggest the truth is we can never find and hold to that; we are always involved in the complicated fraught business of negotiation, of swinging birches, of chasing butterflies, of building walls that will promptly fall down again.














 But Surge itself has since gone through various forms. There were 10 original poems written quickly in 2016. There was a performance piece (at London’s Roundhouse) in the summer of 2017 (it was this version that won the Ted Hughes Award for New Work in poetry in 2017). But it has taken 3 years for this Chatto book to be finalised. In an interview just last year, Bernard observed that they were still unclear what the “final structure” of the material would be. I’m possessed of no insider knowledge on this, but it looks as if this “final” version took some considerable effort – reading it makes me conscious of the strait-jacket that a conventional slim volume of poetry imposes – and I’m not sure the finalised 50-odd pages of the collection really act as the best foil for what are, without doubt, a series of stunningly powerful poems. The blurb and publicity present the book (as publishers so often do) as wholly focused on the New Cross and Grenfell fires but this isn’t really true and something is lost in including the more miscellaneous pieces, particularly towards the end of the book.
But Surge itself has since gone through various forms. There were 10 original poems written quickly in 2016. There was a performance piece (at London’s Roundhouse) in the summer of 2017 (it was this version that won the Ted Hughes Award for New Work in poetry in 2017). But it has taken 3 years for this Chatto book to be finalised. In an interview just last year, Bernard observed that they were still unclear what the “final structure” of the material would be. I’m possessed of no insider knowledge on this, but it looks as if this “final” version took some considerable effort – reading it makes me conscious of the strait-jacket that a conventional slim volume of poetry imposes – and I’m not sure the finalised 50-odd pages of the collection really act as the best foil for what are, without doubt, a series of stunningly powerful poems. The blurb and publicity present the book (as publishers so often do) as wholly focused on the New Cross and Grenfell fires but this isn’t really true and something is lost in including the more miscellaneous pieces, particularly towards the end of the book. Bernard’s poetic voice is at its best when making full use of the licence of free forms, broken grammar, infrequent punctuation, the colloquial voice and often incantatory patois. So a voice in ‘Harbour’ wanders across the page, hesitantly, uncertainly, till images of heat, choking and breaking glass make it clear this is someone caught in the New Cross Fire. Another voice in ‘Clearing’ watches, in the aftermath of the blaze, as an officer collect body parts (including the voice’s own body): “from the bag I watch his face turn away”. The cryptically titled ‘+’ and ‘–’ shift to broken, dialogic prose as a father is asked to identify his dead son through the clothes he was wearing. Then the son’s voice cries out for and watches his father come to the morgue to identify his body. This skilful voice throwing is a vivid way of portraying a variety of individuals and their grief. ‘Kitchen’ offers a calmer voice re-visiting her mother’s house, the details and familiarity evoking simple things that have been lost in the death of the child:
Bernard’s poetic voice is at its best when making full use of the licence of free forms, broken grammar, infrequent punctuation, the colloquial voice and often incantatory patois. So a voice in ‘Harbour’ wanders across the page, hesitantly, uncertainly, till images of heat, choking and breaking glass make it clear this is someone caught in the New Cross Fire. Another voice in ‘Clearing’ watches, in the aftermath of the blaze, as an officer collect body parts (including the voice’s own body): “from the bag I watch his face turn away”. The cryptically titled ‘+’ and ‘–’ shift to broken, dialogic prose as a father is asked to identify his dead son through the clothes he was wearing. Then the son’s voice cries out for and watches his father come to the morgue to identify his body. This skilful voice throwing is a vivid way of portraying a variety of individuals and their grief. ‘Kitchen’ offers a calmer voice re-visiting her mother’s house, the details and familiarity evoking simple things that have been lost in the death of the child: I’m guessing most of the poems I have referred to so far come from the early work of 2016. Other really strong pieces focus on events after the Fire itself. ‘Duppy’ is a sustained description – information slowly drip-fed – of a funeral or memorial meeting and it again becomes clear that the narrative voice is one of the dead: “No-one will tell me what happened to my body”. The title of the poem is a Jamaican word of African origin meaning spirit or ghost. ‘Stone’ is perhaps a rare recurrence of the author’s more autobiographical voice and in its scattered form and absence of punctuation reveals a tactful and beautiful lyrical gift as the narrator visits Fordham Park to sit beside the New Cross Fire’s memorial stone. ‘Songbook II’ is another chanted, hypnotic tribute to one of the mothers of the dead and is probably one of the poems Ali Smith is thinking of when she associates Bernard’s work with that of W.H. Auden.
I’m guessing most of the poems I have referred to so far come from the early work of 2016. Other really strong pieces focus on events after the Fire itself. ‘Duppy’ is a sustained description – information slowly drip-fed – of a funeral or memorial meeting and it again becomes clear that the narrative voice is one of the dead: “No-one will tell me what happened to my body”. The title of the poem is a Jamaican word of African origin meaning spirit or ghost. ‘Stone’ is perhaps a rare recurrence of the author’s more autobiographical voice and in its scattered form and absence of punctuation reveals a tactful and beautiful lyrical gift as the narrator visits Fordham Park to sit beside the New Cross Fire’s memorial stone. ‘Songbook II’ is another chanted, hypnotic tribute to one of the mothers of the dead and is probably one of the poems Ali Smith is thinking of when she associates Bernard’s work with that of W.H. Auden.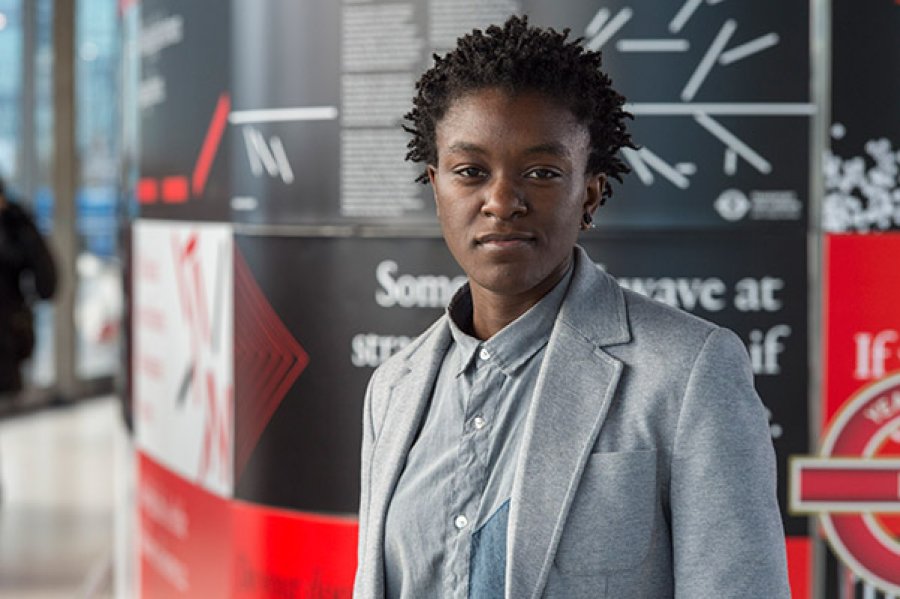 But when the device of haunting and haunted voices is abandoned, Bernard’s work drifts quickly towards the literal and succumbs to the pressure to record events and places (the downside of the archival instinct). A tribute to Naomi Hersi, a black trans-woman found murdered in 2018, sadly doesn’t get much beyond plain location, a kind of reportage and admission that it is difficult to articulate feelings (‘Pem-People’). There are interesting pieces which read as autobiography – a childhood holiday in Jamaica, joining a Pride march, a sexual encounter in Camberwell, but on their own behalf Bernard seems curiously to have lost their eagle eye for the selection of telling details and tone and tension flatten out:
But when the device of haunting and haunted voices is abandoned, Bernard’s work drifts quickly towards the literal and succumbs to the pressure to record events and places (the downside of the archival instinct). A tribute to Naomi Hersi, a black trans-woman found murdered in 2018, sadly doesn’t get much beyond plain location, a kind of reportage and admission that it is difficult to articulate feelings (‘Pem-People’). There are interesting pieces which read as autobiography – a childhood holiday in Jamaica, joining a Pride march, a sexual encounter in Camberwell, but on their own behalf Bernard seems curiously to have lost their eagle eye for the selection of telling details and tone and tension flatten out: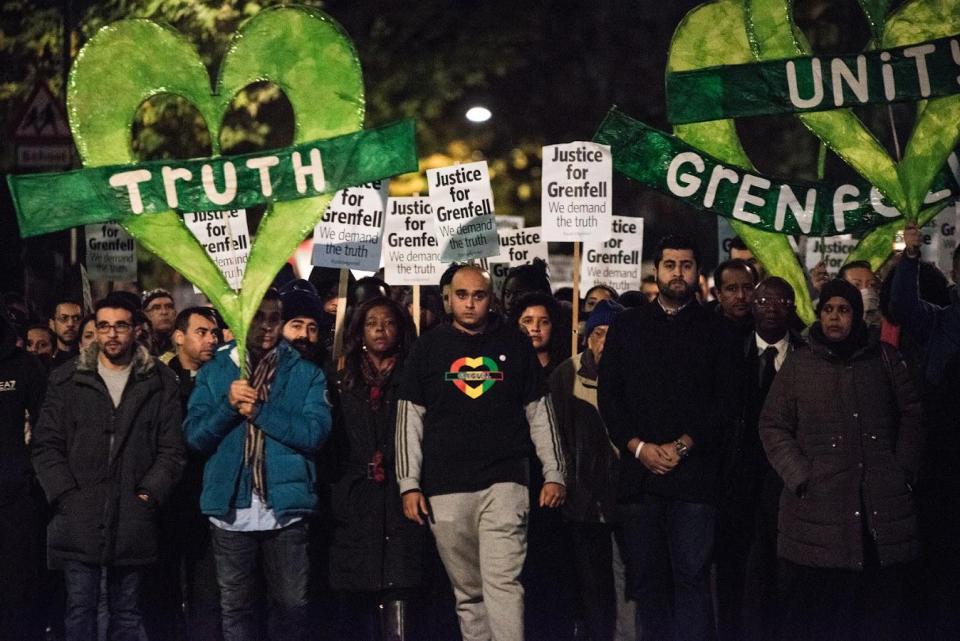 The mirroring architectonic of the collection emerges with the poems written about the Grenfell Tower fire. So we have ‘Ark II’, two pools of prose broken by slashes which seem to be fed by too many tributary streams: the silent marches in Ladbroke grove, the Michael Smithyman murder and abandoned investigation, Smithyman’s transition to Michelle, and the burning of the Grenfell Tower effigy, the video of which emerged in 2018.
The mirroring architectonic of the collection emerges with the poems written about the Grenfell Tower fire. So we have ‘Ark II’, two pools of prose broken by slashes which seem to be fed by too many tributary streams: the silent marches in Ladbroke grove, the Michael Smithyman murder and abandoned investigation, Smithyman’s transition to Michelle, and the burning of the Grenfell Tower effigy, the video of which emerged in 2018.
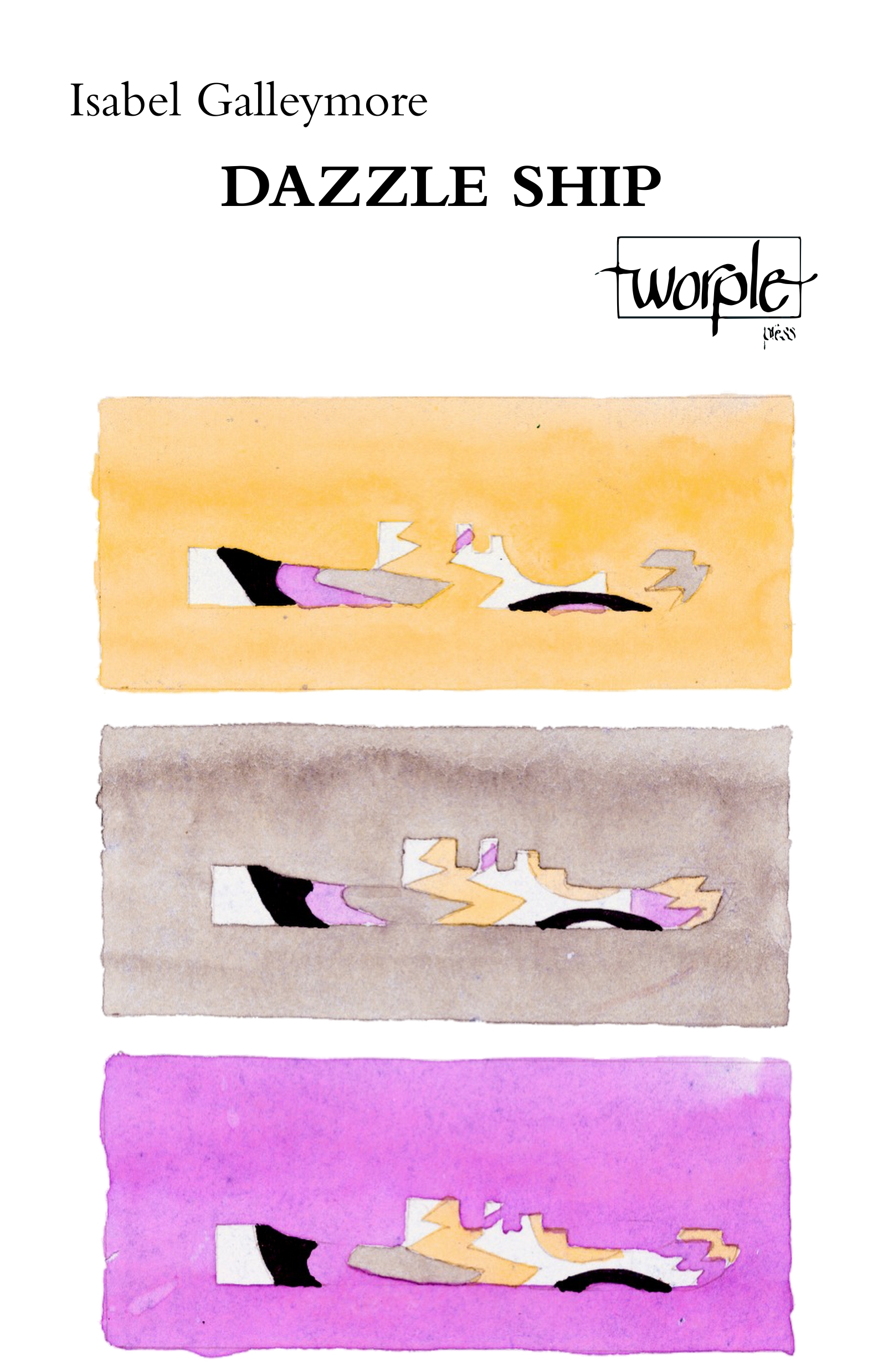





 But Galleymore also sees dangers. In her 2014
But Galleymore also sees dangers. In her 2014 



 Cain also cites the work of Charles Reznikioff and Svetlana Alexievich as models. The former, an Objectivist poet, developed work from
Cain also cites the work of Charles Reznikioff and Svetlana Alexievich as models. The former, an Objectivist poet, developed work from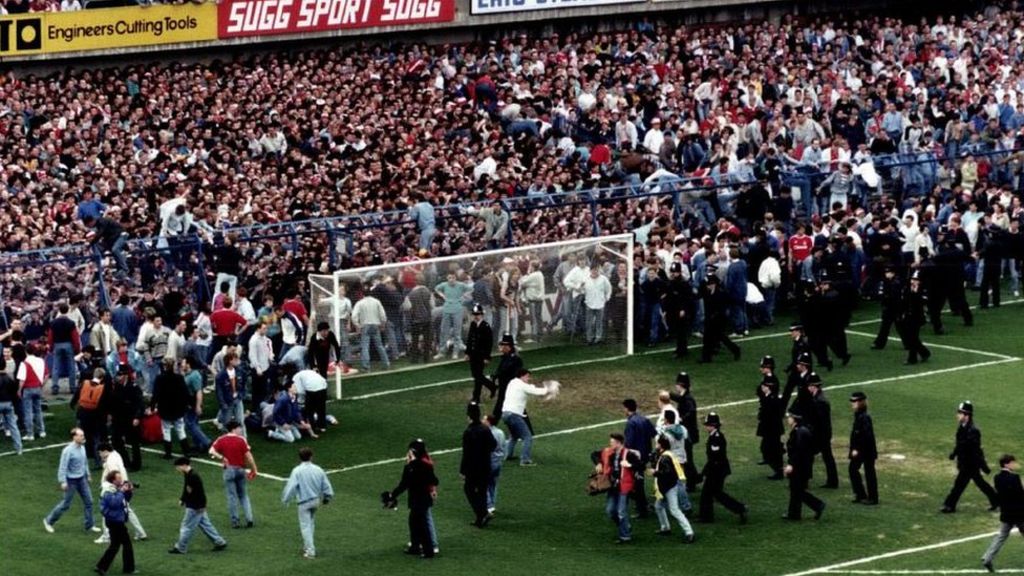 

 In fact – as Cain’s sequence shows – what was being covered up was the original decision of Chief Superintendent David Duckenfield to open the exit gates at 2.47pm. One of his officers spoke to the inquiry: “I was quite shocked // It was totally unprecedented. // It was something you just didn’t do”. This was what caused the inflow of fans – “like sand into an egg timer”. Only at the second inquiry, did Duckenfield revise his earlier false statements: “I didn’t say, // ‘I have authorised the opening of the gates’”.
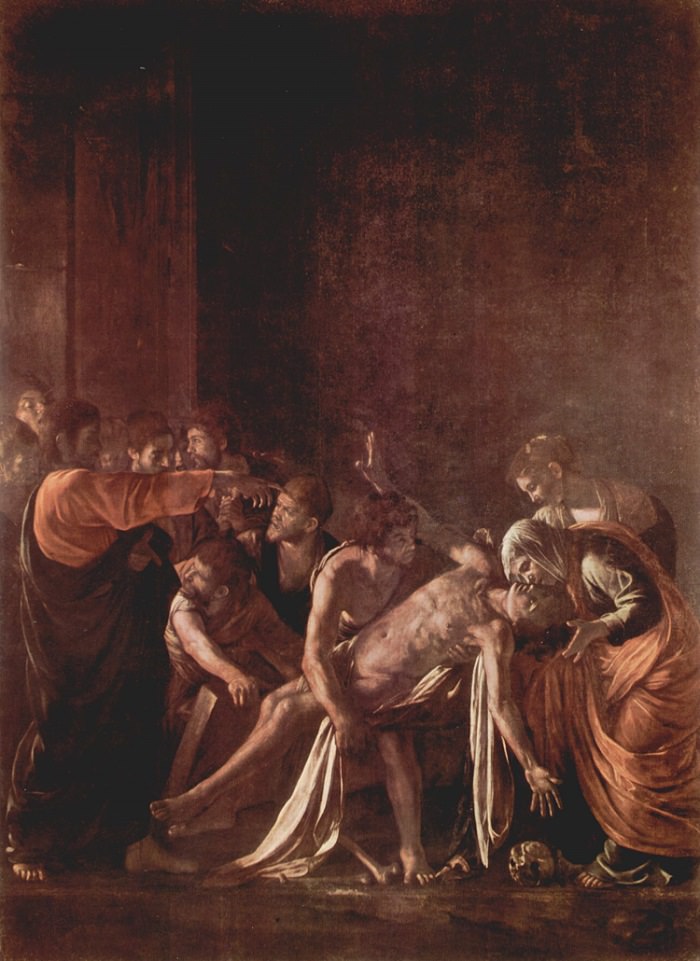
In fact – as Cain’s sequence shows – what was being covered up was the original decision of Chief Superintendent David Duckenfield to open the exit gates at 2.47pm. One of his officers spoke to the inquiry: “I was quite shocked // It was totally unprecedented. // It was something you just didn’t do”. This was what caused the inflow of fans – “like sand into an egg timer”. Only at the second inquiry, did Duckenfield revise his earlier false statements: “I didn’t say, // ‘I have authorised the opening of the gates’”.  David Pollard’s book is divided into three sections, one each on Parmigianino, Rembrandt and Caravaggio. Initially, Pollard presents a set of 15 self-declared “meditations” on a single work of art – Parmigianino’s ‘Self Portrait in a Convex Mirror’ (c. 1524). This is a bold move, given that John Ashbery did the same thing in 1974 and Pollard does explore ideas also found in Ashbery’s poem. Both writers are intrigued by a self-portrait painted onto a half-spherical, contoured surface to simulate a mirror such as was once used by barbers. The viewer gazes at an image of a mirror in which is reflected an image of the artist’s youthful and girlish face. It’s this sense of doubling images – an obvious questioning of what is real – that Pollard begins with. “You are a double-dealer” he declares, addressing the artist directly, though the language is quickly thickened and abstracted into a less than easy, philosophical, meditative style. It is the paradoxes that draw the poet: “you allow the doublings / inherent in your task to hide themselves / in open show, display art that / understands itself too well”. Indeed, this seems to be something of a definition of art for Pollard. “Let us be clear”, he says definitively, though the irony lies in the fact that such art asks questions about clarity precisely to destabilise it.
David Pollard’s book is divided into three sections, one each on Parmigianino, Rembrandt and Caravaggio. Initially, Pollard presents a set of 15 self-declared “meditations” on a single work of art – Parmigianino’s ‘Self Portrait in a Convex Mirror’ (c. 1524). This is a bold move, given that John Ashbery did the same thing in 1974 and Pollard does explore ideas also found in Ashbery’s poem. Both writers are intrigued by a self-portrait painted onto a half-spherical, contoured surface to simulate a mirror such as was once used by barbers. The viewer gazes at an image of a mirror in which is reflected an image of the artist’s youthful and girlish face. It’s this sense of doubling images – an obvious questioning of what is real – that Pollard begins with. “You are a double-dealer” he declares, addressing the artist directly, though the language is quickly thickened and abstracted into a less than easy, philosophical, meditative style. It is the paradoxes that draw the poet: “you allow the doublings / inherent in your task to hide themselves / in open show, display art that / understands itself too well”. Indeed, this seems to be something of a definition of art for Pollard. “Let us be clear”, he says definitively, though the irony lies in the fact that such art asks questions about clarity precisely to destabilise it. The 15 meditations are in free verse, the line endings often destabilising the sense, and they are lightly punctuated when I could have done with more conventional punctuation given the complex, involuted style. Pollard also likes to double up phrases, his second attempt often shifting ground or seeming propelled more by sound than sense. This is what the blurb calls Pollard’s “dense and febrile language” and it is fully self-conscious. In meditation 15, he observes that the artist’s paint is really “composed of almost nothing like words / that in their vanishings leave somewhat / of their meaning” – a ‘somewhat’ that falls well short of anything definitive. Of course, this again echoes Ashbery and appeals to our (post-)modern sensibility. Pollard images such a sense of loss with “a rustle of leaves among the winds / of autumn blowing in circles / back into seasons of the turning world”. He does not possess Ashbery’s originality of image, as here deploying the cliched autumnal leaves and then echoing Eliot’s “still point of the turning world”. Indeed, many poems are frequently allusive (particularly of Shakespearean phrases, Keats coming a close second) and for me this does not really work, the phrases striking as undigested shorthand for things that ought to be more freshly said.
The 15 meditations are in free verse, the line endings often destabilising the sense, and they are lightly punctuated when I could have done with more conventional punctuation given the complex, involuted style. Pollard also likes to double up phrases, his second attempt often shifting ground or seeming propelled more by sound than sense. This is what the blurb calls Pollard’s “dense and febrile language” and it is fully self-conscious. In meditation 15, he observes that the artist’s paint is really “composed of almost nothing like words / that in their vanishings leave somewhat / of their meaning” – a ‘somewhat’ that falls well short of anything definitive. Of course, this again echoes Ashbery and appeals to our (post-)modern sensibility. Pollard images such a sense of loss with “a rustle of leaves among the winds / of autumn blowing in circles / back into seasons of the turning world”. He does not possess Ashbery’s originality of image, as here deploying the cliched autumnal leaves and then echoing Eliot’s “still point of the turning world”. Indeed, many poems are frequently allusive (particularly of Shakespearean phrases, Keats coming a close second) and for me this does not really work, the phrases striking as undigested shorthand for things that ought to be more freshly said.

 In fact, the woman is hardly given a voice and the substance of the sequence is dominated by the (male) artist’s reflections on his years-long task. He’s most often found “between this scaffold floor and ceiling”, complaining about his “craned neck”, pouring plaster, crushing pigments, enumerating at great length the qualities and shades of the paint he employs (Cashman risking an odd parody of a Dulux colour chart at times – “Variety is my clarity, / purity my colour power”). Later, we hear him complaining the plaster will not dry in the cold winter months. We even hear the artist reflecting on his own features, the famous “long white beard and beak-like nose”. These period and technical details work well, but Cashman’s Michelangelo sometimes also shades interestingly into a more future-aware voice, melding – I think – with the poet’s own voice. So he remarks: “Getting lost is not a condition men like me endure or venture on today. / All GPS and mobile interlinks enmesh our every step”. Later, a list of “everything there is” sweepingly includes “chair, man, woman; laptop or confession box”.
In fact, the woman is hardly given a voice and the substance of the sequence is dominated by the (male) artist’s reflections on his years-long task. He’s most often found “between this scaffold floor and ceiling”, complaining about his “craned neck”, pouring plaster, crushing pigments, enumerating at great length the qualities and shades of the paint he employs (Cashman risking an odd parody of a Dulux colour chart at times – “Variety is my clarity, / purity my colour power”). Later, we hear him complaining the plaster will not dry in the cold winter months. We even hear the artist reflecting on his own features, the famous “long white beard and beak-like nose”. These period and technical details work well, but Cashman’s Michelangelo sometimes also shades interestingly into a more future-aware voice, melding – I think – with the poet’s own voice. So he remarks: “Getting lost is not a condition men like me endure or venture on today. / All GPS and mobile interlinks enmesh our every step”. Later, a list of “everything there is” sweepingly includes “chair, man, woman; laptop or confession box”.










