This is how reviews are supposed to work. I recently read James Harpur’s comments on Bonjour Mr Inshaw, published by Two Rivers Press (poems by Peter Robinson, paintings by David Inshaw) in the Spring 2020 issue of Agenda, ‘Pound Reconsidered’. I went out and bought the book.
 I’ve long thought of writing poems about David Inshaw’s paintings, drawn to what Harpur calls his ability to “invest landscapes with spiritual light and energy, balancing realism with a sense of the mythic, of penetrating a noumenal sphere”. The other personal draw to his work has been that Inshaw’s home (and home ground as an artist) is that part of Wiltshire to the west of where I grew up. Inshaw’s home is in Devizes and many of his paintings are of the landscape just a bit further west, of Silbury Hill, Avebury, the barrows and downs of that area. The drive from the M4 turn-off at Hungerford, on the Bath Road, through Marlborough and the A361 to Devizes has long figured in my personal list of favourite drives (not wholly because it was for years the route to my childhood home in Hilperton, Wiltshire). And now Peter Robinson has beaten me to it with this beautiful book of full colour images and 19 poems, though his approach is not simply ekphrastic (merely descriptive of the images) but often launches out from the pictures into concerns shared by the two artists.
I’ve long thought of writing poems about David Inshaw’s paintings, drawn to what Harpur calls his ability to “invest landscapes with spiritual light and energy, balancing realism with a sense of the mythic, of penetrating a noumenal sphere”. The other personal draw to his work has been that Inshaw’s home (and home ground as an artist) is that part of Wiltshire to the west of where I grew up. Inshaw’s home is in Devizes and many of his paintings are of the landscape just a bit further west, of Silbury Hill, Avebury, the barrows and downs of that area. The drive from the M4 turn-off at Hungerford, on the Bath Road, through Marlborough and the A361 to Devizes has long figured in my personal list of favourite drives (not wholly because it was for years the route to my childhood home in Hilperton, Wiltshire). And now Peter Robinson has beaten me to it with this beautiful book of full colour images and 19 poems, though his approach is not simply ekphrastic (merely descriptive of the images) but often launches out from the pictures into concerns shared by the two artists.

Robinson and Inshaw in fact met at Cambridge in the 1970s. That moment is uncertainly recalled in the poem ‘In the Seventies’ (a title borrowed from Thomas Hardy’s poem in Moments of Vision – a sub-theme of this whole book is how both poet and artist respond to Hardy’s work). Various chance meetings over 50 years then occurred including a visit to Devizes in January 2019 during which the project of this book was agreed upon.

The word ‘haunted’ seems to have been designed to be applied to Inshaw’s landscapes. There is a hyper-real quality to the painting which makes the viewer re-see our own surroundings but also takes us through the surface. Harpur’s Agenda review suggested a “Platonic vision” but I’d object to losing the surface of the real so readily. Inshaw was a member of the Brotherhood of Ruralists (here is an old BBC documentary on them – a brilliant example of ‘slow’ TV before it had been thought of) and his landscapes are usually peopled and the trees and downs and ancient memorials are therefore always ‘seen’. Inshaw’s work is about time and memory (Hardy again) and the way moments of vision or perception can feel heightened. The poem ‘Haunting Landscapes’ alludes to Inshaw’s ‘Our days were a joy and our paths through flowers’ (another quote from Hardy, his poem ‘After a Journey’). A woman in black stands in a graveyard but has turned as if being called to from beyond the frame (by a memory, a ghost).

As in so many memories, there is a heightened particularity to Inshaw’s paintings. There is a Rilkean focus on what ‘The Kennet’ calls “being here”. Look at Inshaw’s ‘Tree and Moon’, for example, and Robinson’s accompanying poem, ‘At Slader’s Yard’, associates the two artists (and their art forms) in the quality of their ‘noticing’: “I’m a counter of clouds / come over the hills like this one / ‘salmoning’ in a ‘deepening blue’”. Hardy’s poem ‘Afterwards’ describes himself as a “man who . . . noticed things”. Robinson’s concluding poem, ‘After a Visit’, suggests how Inshaw’s precision of observation (“the starkness of those winter branches’ / black against a glowing skyline”) manages to inculcate a sense of something other than mere perception of colour and shape: “it brings back the sense of some design, / and a meaning to this scene”. The root and pattern of design is unclear. The value of such a comprehending vision is heightened by the precise historical context in which many of these poems were written. The divisions and confusions of Brexit and the world of Covid infection and lockdowns keeps breaking through the surface of this book. The parliamentary “palaver”, hypocritically urging us to “come together as a nation” and a certain politician, “pre-disgraced”, indicate that neither poet nor painter look upon the landscape of southern England with their heads in the clouds, nor with any narrowly nostalgic gaze.

 I’m not proud to admit that Way More Than Luck passed me by when it was first published. As you are probably aware, Wilkinson reviews poetry regularly for The Guardian, and he’s very familiar on social media as a poet and critic, a distance runner and a passionate Liverpool football fan. But the book’s cover (Dalglish, I think), its title and some of the publicity persuaded me that the football bit was going to be predominant. It’s certainly an almost unique aspect of the collection, but it turns out the debilitating darkness of psychological depression is an even more significant one. Wilkinson signals this concern via the book’s two epigraphs. One is about the nature of depression
I’m not proud to admit that Way More Than Luck passed me by when it was first published. As you are probably aware, Wilkinson reviews poetry regularly for The Guardian, and he’s very familiar on social media as a poet and critic, a distance runner and a passionate Liverpool football fan. But the book’s cover (Dalglish, I think), its title and some of the publicity persuaded me that the football bit was going to be predominant. It’s certainly an almost unique aspect of the collection, but it turns out the debilitating darkness of psychological depression is an even more significant one. Wilkinson signals this concern via the book’s two epigraphs. One is about the nature of depression 

 For me, it’s these psychological truths that Wilkinson is so good at conveying. There are other poems later in the book (and perhaps ‘Stag’ is an elusive example) which begin to sketch episodes of a foundering romantic relationship and ‘Building a Brighter, More Secure Future’ is a very effective excursion into witty political satire (a skilfully handled sestina based on the Conservative Party election manifesto, 2015). And there are the football poems. They comprise the central sequence of 14 poems, introduced with a heart-felt Prologue that says what follows is for the ordinary football fans, written out of “a love beyond the smear campaigns, / the media’s hooligans”. A large part of what Wilkinson has in mind here is the shocking response in parts of the media to the Hillsborough tragedy in 1989, when 96 men, women and children died (David Cain’s Forward prize shortlisted book, Truth Street, from Smokestack Books, movingly dealt with this event and the media and policing responses and
For me, it’s these psychological truths that Wilkinson is so good at conveying. There are other poems later in the book (and perhaps ‘Stag’ is an elusive example) which begin to sketch episodes of a foundering romantic relationship and ‘Building a Brighter, More Secure Future’ is a very effective excursion into witty political satire (a skilfully handled sestina based on the Conservative Party election manifesto, 2015). And there are the football poems. They comprise the central sequence of 14 poems, introduced with a heart-felt Prologue that says what follows is for the ordinary football fans, written out of “a love beyond the smear campaigns, / the media’s hooligans”. A large part of what Wilkinson has in mind here is the shocking response in parts of the media to the Hillsborough tragedy in 1989, when 96 men, women and children died (David Cain’s Forward prize shortlisted book, Truth Street, from Smokestack Books, movingly dealt with this event and the media and policing responses and  But the poems also show how difficult it is to escape the miasma of cliché that seems to engulf football itself. Anfield is filled with a “fabled buzz”, then “the place erupt[s]”. Barnes unleashes a “a sweeping, goal-bound ball”, and a particular game offers one “last-ditch twist”. I’m reminded of Louis MacNeice’s observation (now sadly compromised in various ways, but the spirit of it remains valid, I think) that he wanted a poet not to be “too esoteric. I would have a poet able-bodied [sic], fond of talking, a reader of the newspapers, capable of pity and laughter, informed in economics, appreciative of women [sic], involved in personal relationships, actively interested in politics, susceptible to physical impressions’. There are many more of these poets around these days and to bring (even) football into the purview of poetry can hardly be a bad thing. Yet it is not an easy one and there may be some risks in deciding to headline the attempt. Ian Duhig’s blurb note to Way More Than Luck has gingerly to negotiate this issue: “The beautiful game inspires some beautiful poems in Ben Wilkinson’s terrific debut collection … but there’s far more than football to focus on here”. Yes, indeed.
But the poems also show how difficult it is to escape the miasma of cliché that seems to engulf football itself. Anfield is filled with a “fabled buzz”, then “the place erupt[s]”. Barnes unleashes a “a sweeping, goal-bound ball”, and a particular game offers one “last-ditch twist”. I’m reminded of Louis MacNeice’s observation (now sadly compromised in various ways, but the spirit of it remains valid, I think) that he wanted a poet not to be “too esoteric. I would have a poet able-bodied [sic], fond of talking, a reader of the newspapers, capable of pity and laughter, informed in economics, appreciative of women [sic], involved in personal relationships, actively interested in politics, susceptible to physical impressions’. There are many more of these poets around these days and to bring (even) football into the purview of poetry can hardly be a bad thing. Yet it is not an easy one and there may be some risks in deciding to headline the attempt. Ian Duhig’s blurb note to Way More Than Luck has gingerly to negotiate this issue: “The beautiful game inspires some beautiful poems in Ben Wilkinson’s terrific debut collection … but there’s far more than football to focus on here”. Yes, indeed. I am very grateful to Ian Brinton’s and Michael Grant’s recent translation of a selected Mallarmé (Muscaliet, 2019) for sending me back to a poet who has always proved problematic for me. My natural inclination draws me more to Louis MacNeice’s sense of the “drunkenness of things being various” (‘Snow’) – his emphasis on poetry’s engagement with “things” – and his desire to communicate pretty directly with his fellow wo/man, than with what Elizabeth McCombie bluntly calls “the exceptional difficulty” of Mallarmé’s work. I appreciate that such a dichotomy seems to shove the French poet into an ivory tower (albeit of glittering and sensuous language) while casting the Irish one as too narrowly engagé, but I’m also aware that Sartre praised Mallarmé as a “committed” writer and that, despite some evident remoteness from the ‘tribe’, the French poet’s political views were both radical and democratic.
I am very grateful to Ian Brinton’s and Michael Grant’s recent translation of a selected Mallarmé (Muscaliet, 2019) for sending me back to a poet who has always proved problematic for me. My natural inclination draws me more to Louis MacNeice’s sense of the “drunkenness of things being various” (‘Snow’) – his emphasis on poetry’s engagement with “things” – and his desire to communicate pretty directly with his fellow wo/man, than with what Elizabeth McCombie bluntly calls “the exceptional difficulty” of Mallarmé’s work. I appreciate that such a dichotomy seems to shove the French poet into an ivory tower (albeit of glittering and sensuous language) while casting the Irish one as too narrowly engagé, but I’m also aware that Sartre praised Mallarmé as a “committed” writer and that, despite some evident remoteness from the ‘tribe’, the French poet’s political views were both radical and democratic. So, if we must give up on such ‘understanding’, what was Mallarmé – writing in the 1880-90s – doing? Something recognisably very modern, it turns out. Contra Wordsworth (and MacNeice, I guess), Mallarmé and his Symbolist peers, held ordinary language in suspicious contempt as too ‘journalistic’, too wedded to a world of facts. Poetry was to be more a communication, or evocation, of emotion, of a detachment from the (merely) everyday and a recovery of the mystery of existence which rote and routine has served to bury. Such a role demanded linguistic innovation as suggested in ‘The Tomb of Edgar Poe’ in which the American writer is praised for giving “purer meaning to the words of the tribe” (tr. Brinton/Grant). Writing about Edouard Manet’s work, Mallarmé saw the need to “loose the restraint of education” which – in linguistic terms – would mean freeing language from its contingent relations to the facticity of things (and the tedium and ennui that results from our long confinement to them) and hence moving language nearer to what he called the “Idea” and the paradoxical term Nothingness (as Brinton/Grant translate “le Neant”).
So, if we must give up on such ‘understanding’, what was Mallarmé – writing in the 1880-90s – doing? Something recognisably very modern, it turns out. Contra Wordsworth (and MacNeice, I guess), Mallarmé and his Symbolist peers, held ordinary language in suspicious contempt as too ‘journalistic’, too wedded to a world of facts. Poetry was to be more a communication, or evocation, of emotion, of a detachment from the (merely) everyday and a recovery of the mystery of existence which rote and routine has served to bury. Such a role demanded linguistic innovation as suggested in ‘The Tomb of Edgar Poe’ in which the American writer is praised for giving “purer meaning to the words of the tribe” (tr. Brinton/Grant). Writing about Edouard Manet’s work, Mallarmé saw the need to “loose the restraint of education” which – in linguistic terms – would mean freeing language from its contingent relations to the facticity of things (and the tedium and ennui that results from our long confinement to them) and hence moving language nearer to what he called the “Idea” and the paradoxical term Nothingness (as Brinton/Grant translate “le Neant”). For these reasons, Mallarmé “cede[s] the initiative to words” (‘Crise de Vers’), to language’s material aspects as much as to its referential functions. Carrying over the material aspects of his French verse into English is then, to say the least, difficult. I’m inclined to agree with Weinfield (Introduction to Stephane Mallarmé Collected Poems (Uni. Of California Press, 1994) that it is “essential to work in rhyme and metre, regardless of the semantic accommodations and technical problems this entail[s]. If we take rhyme from Mallarmé, we take away the poetry”. But is that even possible? The accommodations and problems that arise are huge! Mallarmé placed the sonnet, ‘Salut’, at the start of his Poésies as a toast, salutation and mission statement. Weinfield gives the sestet as follows:
For these reasons, Mallarmé “cede[s] the initiative to words” (‘Crise de Vers’), to language’s material aspects as much as to its referential functions. Carrying over the material aspects of his French verse into English is then, to say the least, difficult. I’m inclined to agree with Weinfield (Introduction to Stephane Mallarmé Collected Poems (Uni. Of California Press, 1994) that it is “essential to work in rhyme and metre, regardless of the semantic accommodations and technical problems this entail[s]. If we take rhyme from Mallarmé, we take away the poetry”. But is that even possible? The accommodations and problems that arise are huge! Mallarmé placed the sonnet, ‘Salut’, at the start of his Poésies as a toast, salutation and mission statement. Weinfield gives the sestet as follows:
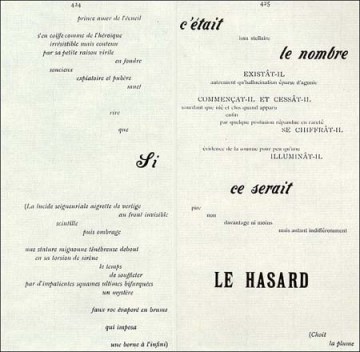




 I
I In lieu of a new blog post, here is a link to the Hercules Editions webpage on which I have formulated a few thoughts about the current lockdown, photography and the (forgotten?) refugee crisis in the Mediterranean. It is a piece in part related to the Hercules publication of my longer poem,
In lieu of a new blog post, here is a link to the Hercules Editions webpage on which I have formulated a few thoughts about the current lockdown, photography and the (forgotten?) refugee crisis in the Mediterranean. It is a piece in part related to the Hercules publication of my longer poem, 






 But Surge itself has since gone through various forms. There were 10 original poems written quickly in 2016. There was a performance piece (at London’s Roundhouse) in the summer of 2017 (it was this version that won the Ted Hughes Award for New Work in poetry in 2017). But it has taken 3 years for this Chatto book to be finalised. In an interview just last year, Bernard observed that they were still unclear what the “final structure” of the material would be. I’m possessed of no insider knowledge on this, but it looks as if this “final” version took some considerable effort – reading it makes me conscious of the strait-jacket that a conventional slim volume of poetry imposes – and I’m not sure the finalised 50-odd pages of the collection really act as the best foil for what are, without doubt, a series of stunningly powerful poems. The blurb and publicity present the book (as publishers so often do) as wholly focused on the New Cross and Grenfell fires but this isn’t really true and something is lost in including the more miscellaneous pieces, particularly towards the end of the book.
But Surge itself has since gone through various forms. There were 10 original poems written quickly in 2016. There was a performance piece (at London’s Roundhouse) in the summer of 2017 (it was this version that won the Ted Hughes Award for New Work in poetry in 2017). But it has taken 3 years for this Chatto book to be finalised. In an interview just last year, Bernard observed that they were still unclear what the “final structure” of the material would be. I’m possessed of no insider knowledge on this, but it looks as if this “final” version took some considerable effort – reading it makes me conscious of the strait-jacket that a conventional slim volume of poetry imposes – and I’m not sure the finalised 50-odd pages of the collection really act as the best foil for what are, without doubt, a series of stunningly powerful poems. The blurb and publicity present the book (as publishers so often do) as wholly focused on the New Cross and Grenfell fires but this isn’t really true and something is lost in including the more miscellaneous pieces, particularly towards the end of the book. Bernard’s poetic voice is at its best when making full use of the licence of free forms, broken grammar, infrequent punctuation, the colloquial voice and often incantatory patois. So a voice in ‘Harbour’ wanders across the page, hesitantly, uncertainly, till images of heat, choking and breaking glass make it clear this is someone caught in the New Cross Fire. Another voice in ‘Clearing’ watches, in the aftermath of the blaze, as an officer collect body parts (including the voice’s own body): “from the bag I watch his face turn away”. The cryptically titled ‘+’ and ‘–’ shift to broken, dialogic prose as a father is asked to identify his dead son through the clothes he was wearing. Then the son’s voice cries out for and watches his father come to the morgue to identify his body. This skilful voice throwing is a vivid way of portraying a variety of individuals and their grief. ‘Kitchen’ offers a calmer voice re-visiting her mother’s house, the details and familiarity evoking simple things that have been lost in the death of the child:
Bernard’s poetic voice is at its best when making full use of the licence of free forms, broken grammar, infrequent punctuation, the colloquial voice and often incantatory patois. So a voice in ‘Harbour’ wanders across the page, hesitantly, uncertainly, till images of heat, choking and breaking glass make it clear this is someone caught in the New Cross Fire. Another voice in ‘Clearing’ watches, in the aftermath of the blaze, as an officer collect body parts (including the voice’s own body): “from the bag I watch his face turn away”. The cryptically titled ‘+’ and ‘–’ shift to broken, dialogic prose as a father is asked to identify his dead son through the clothes he was wearing. Then the son’s voice cries out for and watches his father come to the morgue to identify his body. This skilful voice throwing is a vivid way of portraying a variety of individuals and their grief. ‘Kitchen’ offers a calmer voice re-visiting her mother’s house, the details and familiarity evoking simple things that have been lost in the death of the child: I’m guessing most of the poems I have referred to so far come from the early work of 2016. Other really strong pieces focus on events after the Fire itself. ‘Duppy’ is a sustained description – information slowly drip-fed – of a funeral or memorial meeting and it again becomes clear that the narrative voice is one of the dead: “No-one will tell me what happened to my body”. The title of the poem is a Jamaican word of African origin meaning spirit or ghost. ‘Stone’ is perhaps a rare recurrence of the author’s more autobiographical voice and in its scattered form and absence of punctuation reveals a tactful and beautiful lyrical gift as the narrator visits Fordham Park to sit beside the New Cross Fire’s memorial stone. ‘Songbook II’ is another chanted, hypnotic tribute to one of the mothers of the dead and is probably one of the poems Ali Smith is thinking of when she associates Bernard’s work with that of W.H. Auden.
I’m guessing most of the poems I have referred to so far come from the early work of 2016. Other really strong pieces focus on events after the Fire itself. ‘Duppy’ is a sustained description – information slowly drip-fed – of a funeral or memorial meeting and it again becomes clear that the narrative voice is one of the dead: “No-one will tell me what happened to my body”. The title of the poem is a Jamaican word of African origin meaning spirit or ghost. ‘Stone’ is perhaps a rare recurrence of the author’s more autobiographical voice and in its scattered form and absence of punctuation reveals a tactful and beautiful lyrical gift as the narrator visits Fordham Park to sit beside the New Cross Fire’s memorial stone. ‘Songbook II’ is another chanted, hypnotic tribute to one of the mothers of the dead and is probably one of the poems Ali Smith is thinking of when she associates Bernard’s work with that of W.H. Auden. But when the device of haunting and haunted voices is abandoned, Bernard’s work drifts quickly towards the literal and succumbs to the pressure to record events and places (the downside of the archival instinct). A tribute to Naomi Hersi, a black trans-woman found murdered in 2018, sadly doesn’t get much beyond plain location, a kind of reportage and admission that it is difficult to articulate feelings (‘Pem-People’). There are interesting pieces which read as autobiography – a childhood holiday in Jamaica, joining a Pride march, a sexual encounter in Camberwell, but on their own behalf Bernard seems curiously to have lost their eagle eye for the selection of telling details and tone and tension flatten out:
But when the device of haunting and haunted voices is abandoned, Bernard’s work drifts quickly towards the literal and succumbs to the pressure to record events and places (the downside of the archival instinct). A tribute to Naomi Hersi, a black trans-woman found murdered in 2018, sadly doesn’t get much beyond plain location, a kind of reportage and admission that it is difficult to articulate feelings (‘Pem-People’). There are interesting pieces which read as autobiography – a childhood holiday in Jamaica, joining a Pride march, a sexual encounter in Camberwell, but on their own behalf Bernard seems curiously to have lost their eagle eye for the selection of telling details and tone and tension flatten out: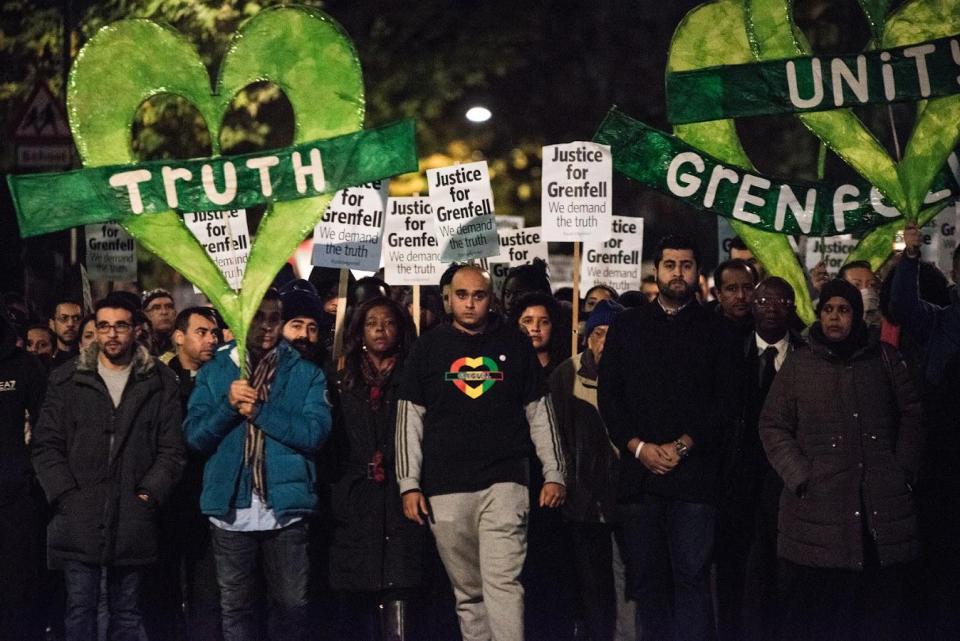 The mirroring architectonic of the collection emerges with the poems written about the Grenfell Tower fire. So we have ‘Ark II’, two pools of prose broken by slashes which seem to be fed by too many tributary streams: the silent marches in Ladbroke grove, the Michael Smithyman murder and abandoned investigation, Smithyman’s transition to Michelle, and the burning of the Grenfell Tower effigy, the video of which emerged in 2018.
The mirroring architectonic of the collection emerges with the poems written about the Grenfell Tower fire. So we have ‘Ark II’, two pools of prose broken by slashes which seem to be fed by too many tributary streams: the silent marches in Ladbroke grove, the Michael Smithyman murder and abandoned investigation, Smithyman’s transition to Michelle, and the burning of the Grenfell Tower effigy, the video of which emerged in 2018.





 But Galleymore also sees dangers. In her 2014
But Galleymore also sees dangers. In her 2014 

