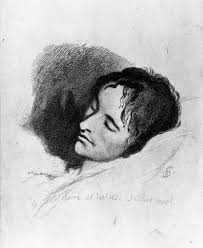
Hesperus Press are just about to publish Will Stone’s eminently readable and wonderfully grounded translation of a contemporary account of Friedrich Holderlin’s madness. This is a long essay by Wilhelm Waiblinger, written in Rome during the winter of 1827/8. It’s an astonishing and very moving document for those interested in German Romantic and Modern poetry or in early accounts of mental illness or – as I am aware is my own case – for those who will instantly recognise, in these brilliant and detailed observations, some of the behavioural elements of what we now loosely refer to as dementia.

The essay first appeared in 1831, ironically only a year after its author’s death, though still a dozen years before its subject’s demise. Stone’s excellent introduction tells us that Waiblinger was an up-and-coming poet of the 1820s, “a rebel, a wayward fellow and a liberal maverick”. He studied at the same Protestant seminary (the ‘Tubinger Stift’) where Holderlin had studied from 1788 with Schelling and Hegel (imagine that team on University Challenge). But by 1806, the older poet had been confined to his tower in Tubingen (the ‘Holderlinturm’) because considered incurably mad. Waiblinger began visiting him in the summer of 1822. For four years, he saw Holderlin close-up, walking with him, trying to talk with him and enduring some pretty wild-sounding piano playing too.
 Waiblinger was a real Holderlin fan. The older poet’s novel, Hyperion, had appeared in 1822 (I review a recent translation of it here) and the younger man found it “saturated with spirit: a fervent fully glowing soul swells there” He was swept away: “Holderlin shakes me to the core. I find in him an eternally rich form of sustenance”. The mad poet in his tower was not often amenable to being visited, but Waiblinger, for some reason, proved an exception: “This lunatic, sitting at the window [. . .] is far closer to me”, the young man wrote, “than the thousands out there who are said to be sane”. Stone makes it clear that Waiblinger not only admired Hyperion but voiced the need for Holderlin’s other poetry to be re-published. Gradually, having fallen into obscurity, “his special hymnic style, fusing Greek myth and Romantic mysticism” eventually started to attract new admirers including Nietzsche, Schumann, Brahms, Rilke, Hesse, Trakl, Benjamin and Celan.
Waiblinger was a real Holderlin fan. The older poet’s novel, Hyperion, had appeared in 1822 (I review a recent translation of it here) and the younger man found it “saturated with spirit: a fervent fully glowing soul swells there” He was swept away: “Holderlin shakes me to the core. I find in him an eternally rich form of sustenance”. The mad poet in his tower was not often amenable to being visited, but Waiblinger, for some reason, proved an exception: “This lunatic, sitting at the window [. . .] is far closer to me”, the young man wrote, “than the thousands out there who are said to be sane”. Stone makes it clear that Waiblinger not only admired Hyperion but voiced the need for Holderlin’s other poetry to be re-published. Gradually, having fallen into obscurity, “his special hymnic style, fusing Greek myth and Romantic mysticism” eventually started to attract new admirers including Nietzsche, Schumann, Brahms, Rilke, Hesse, Trakl, Benjamin and Celan.
Initially, Waiblinger seems to have intended to document: “It is not my place to offer some profound psychological insight, but rather to limit the quest to simple observation, a modest character sketch”. Filling in Holderlin’s earlier years he notes the uniqueness of his work in his “enthusiasm for Greek antiquity” which “left [its] mark on the tonality of his own creations” and led to a sense “of discontentment with the land of his birth”. This kind of sentiment dominates Hyperion and Waiblinger (sounding a bit prissily patriotic here) finds it elicits in him “a certain repugnance”. Waiblinger also reminds us of Holderlin’s doomed affair with the already-married Susette Gontard (the model for the Diotima figure in the poems and Hyperion). He sees the termination of the affair as the main contributory factor in Holderlin’s decline: “The coddled youth, lulled by the sweet intoxication of this love entanglement, was suddenly pitched back into bitter reality”. From here on, Holderlin was to carry “a fracture in his heart”, a wound barely transformed in Hyperion which Waiblinger reads as documenting “an unnatural struggle against destiny, a wounded mawkishness, a black melancholy and an ill-fated perverseness [that] cleaves a path into madness”.

No doubt the end of the affair did deeply affect Holderlin, but Waiblinger’s drawing a direct line from it to the ‘Holderlinturm’ is probably a bit simplistic. Sheltered from the “bitter reality” outside the tower, Holderlin continued to write letters in prose and verse. Given the period, it’s not surprising to hear Waiblinger describe the mockery of locals who caught Holderlin out walking – and good to hear that the old poet responded with mud and stones thrown at his attackers. Yet his behaviour was often like that of a small child: “When he leaves the house, they have to remind him in advance to wash and groom himself, for his hands are habitually soiled from spending half the day tearing up grass”. This tearing up grass seems to have been a common occupation as does, while out walking, flapping his handkerchief against fence posts. All the while, “he talks incessantly to himself, questioning and responding, sometimes yes sometimes no, and often both at the same time”.
One of Holderlin’s other occupations in his madness was re-reading his own Hyperion. He would read aloud, exclaiming “Wonderful, wonderful!” then go on, pausing only to remark, “You see gracious sir, a comma!” In true Romantic style, Waiblinger notices that the mad poet is more calm and more lucid in the open air: “he spoke to himself less [. . .] I was convinced this unceasing monologue with himself was nothing more than the disequilibrium of thought and his inability to gain significant purchase on any object”. For those who have witnessed a relative or friend suffering from dementia, this is a familiar thought and familiar also, perhaps, is the recourse to the phrase “It’s of no consequence to me” which Waiblinger heard repeatedly from the chattering Holderlin.
Playing a piano still gave him some pleasure it seems, beginning in childish simplicity, playing the same theme over and over hundreds of times. On other occasions, almost in spasmodic fits, he’d race across the keyboard, his long, uncut fingernails making an “unpleasant clattering sound”! He would also sing with great pathos – though not in any identifiable language. Holderlin’s family had completely abandoned him in his madness, but Waiblinger records him writing to his mother in the style of a child, “who cannot write in a fully developed way or sustain a thought”.

In fact, Waiblinger suggests that Holderlin’s difficulties lay in mental weakness rather than full-blown insanity. He is “incapable of holding a thought, of giving it clarity, of following it and linking it to another by way of analogy and thus to articulate a distant idea in a regular consistent sequence”. He has another go at describing what he imagines must be going on: “He wishes to affirm something, but since reality [. . .] does not concern him, he refuses it at the same moment, for his spirit is a realm which sustains only fog and what is feigned”. This is partly evident because of Holderlin’s habit (in his madness) of thinking out loud, so Waiblinger believes he can hear a thought being consumed even in the moment of its conception. In the grip of such fluidity and terrifying fog, Holderlin then would shake his head and cry out ‘No, no!’ and begin “firing out words without meaning or any signification, as if his spirit, in a sense overstretched by such a drawn-out thought, could restore itself only by having his mouth issue words which bore no relation to any of it”. Holderlin retreats from his own incoherence into the comfort of sheer random association.

The results are inevitable for the patient and (again recognisably) yield up a fierce, walled-in, self-involvement. Waiblinger describes a “complete lack of participation in and interest for any events outside himself”, and this, alongside an “incapacity to wish to grasp, recognise, understand, to allow in another individuality other than his own”, means there is no possibility of rational communication with the patient. And such solitude – experienced from the inside – results in such boredom that “he needs to speak to himself”, though lacking the ability to follow one thing with anything coherent, the result is “diabolical confusion” and mere “gibberish”. So it’s with some surprise that we find Waiblinger ending his essay with any thought at all of Holderlin’s recovery. He admits it’s unlikely – but does allow himself (surely consoling himself) with imagining an occasional “momentary restoration”, though even this might only be brief, perhaps no more than a fleeting prelude to the moment of death.
But perhaps such imagined lucid moments are less than consoling to those who spend time observing such distress. Leafing through his papers, Waiblinger says he discovered a quite terrifying phrase. Holderlin at one moment had scrawled down, “Now for the first time I understand humankind, because I dwell far from it and in solitude”. It is almost unbearably moving to imagine such flashes of conscious insight coming to the old poet in the midst of so much mental confusion and perceptual fragmentation. What Waiblinger here describes feels bang up to date and yet must be as old as the hills. Will Stone has done an important job in bringing this essay into English.


![moulin-glacier-11[2]](https://martyncrucefix.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/moulin-glacier-112.jpg?w=352&h=264)





 Another young female narrator deliberately stays at home while her parents (conventionally) go to church on Sundays. She’s a teenage rebel without a cause as “The truth is I’m not sure what I did / those mornings”. The poem is built from a list (one of Littlefair’s favourite forms) of what she did and did not do. Littlefair is almost always good with her figurative language and here the girl is variously an undone shoelace, an open rucksack, a blunt knife. The urge to non-conformity outruns her imagination as to how she might spend her growing independence and there is an interesting tension at the last as her parents return, “whole” having “sung their hallelujahs” while the young girl is till restlessly revising her choice of nail polish, as yet unable to find what she’s after.
Another young female narrator deliberately stays at home while her parents (conventionally) go to church on Sundays. She’s a teenage rebel without a cause as “The truth is I’m not sure what I did / those mornings”. The poem is built from a list (one of Littlefair’s favourite forms) of what she did and did not do. Littlefair is almost always good with her figurative language and here the girl is variously an undone shoelace, an open rucksack, a blunt knife. The urge to non-conformity outruns her imagination as to how she might spend her growing independence and there is an interesting tension at the last as her parents return, “whole” having “sung their hallelujahs” while the young girl is till restlessly revising her choice of nail polish, as yet unable to find what she’s after.
 I think I find this with some other poems too, though it’s partly because Littlefair is admirably intent on presenting the working world, the world of labour, as routine in contrast to the allure of a more adventurous life. ‘Assignment brief’ presents itself as an old familiar’s introduction to a new girl’s routine office job; the lists and proffered options are funny but they slowly run out of steam. Likewise, the promisingly titled ‘Usually, I’m a different person at this party’ flags latterly. I’m imagining this as narrated by an older version of the girl who half fell in love with Tara Miller. Here, she shadow-boxes the risks of conventionality by over-insisting on her own sweeping and glamorous life, in the process claiming all sorts of ‘interesting’ aspects of herself: “I only ever have large and sweeping illnesses. / My lymph nodes swell glamorously. I never snuffle”. But the contrasts here are again rather roughly hewn and, in the end, close to cartoonish.
I think I find this with some other poems too, though it’s partly because Littlefair is admirably intent on presenting the working world, the world of labour, as routine in contrast to the allure of a more adventurous life. ‘Assignment brief’ presents itself as an old familiar’s introduction to a new girl’s routine office job; the lists and proffered options are funny but they slowly run out of steam. Likewise, the promisingly titled ‘Usually, I’m a different person at this party’ flags latterly. I’m imagining this as narrated by an older version of the girl who half fell in love with Tara Miller. Here, she shadow-boxes the risks of conventionality by over-insisting on her own sweeping and glamorous life, in the process claiming all sorts of ‘interesting’ aspects of herself: “I only ever have large and sweeping illnesses. / My lymph nodes swell glamorously. I never snuffle”. But the contrasts here are again rather roughly hewn and, in the end, close to cartoonish. The latter view is more than a possibility given that Littlefair’s poems also boldly explore the self’s relation with itself. The encounter between self and future self is plainly and humorously told in ‘Visitations from future self’ and it finds the present self in trouble, pleading “I can’t go on / like this, my life a tap that won’t / switch on”. Here, the present self’s cliched and optimistic hopes for a “rain-before-the-rainbow thing” are denigrated and stared down by the future self. ‘Sertraline’ echoes Plath’s The Bell Jar in its evocation of a summer spent on an anti-depressive drug. And ‘Giraffe’ itself is a prose poem (there are 3 prose pieces in the whole book) in which a voice is offering reassurances to someone hoping to “feel better”. In a final list, images of a return to ‘health’ are offered. Particularly good is the idea that suffering will remain a fact but “your sadness will be graspable, roadworthy, have handlebars”. And lastly, “When you feel better, you will not always be happy, but when happiness does come, it will be long-legged, sun-dappled: a giraffe.”
The latter view is more than a possibility given that Littlefair’s poems also boldly explore the self’s relation with itself. The encounter between self and future self is plainly and humorously told in ‘Visitations from future self’ and it finds the present self in trouble, pleading “I can’t go on / like this, my life a tap that won’t / switch on”. Here, the present self’s cliched and optimistic hopes for a “rain-before-the-rainbow thing” are denigrated and stared down by the future self. ‘Sertraline’ echoes Plath’s The Bell Jar in its evocation of a summer spent on an anti-depressive drug. And ‘Giraffe’ itself is a prose poem (there are 3 prose pieces in the whole book) in which a voice is offering reassurances to someone hoping to “feel better”. In a final list, images of a return to ‘health’ are offered. Particularly good is the idea that suffering will remain a fact but “your sadness will be graspable, roadworthy, have handlebars”. And lastly, “When you feel better, you will not always be happy, but when happiness does come, it will be long-legged, sun-dappled: a giraffe.” The designation ‘a young poet to watch’ is over-used but on this occasion it needs to be said loudly. Giraffe contains a number of fresh, intriguing and fully-achieved poems. It’s well worth seeking out. I well remember reading and being very impressed by Liz Berry’s 2010 Tall Lighthouse debut chapbook, the patron saint of schoolgirls, and this selection from Bryony Littlefair’s early work runs it close. My review of Liz Berry’s subsequent, prize-winning full collection,
The designation ‘a young poet to watch’ is over-used but on this occasion it needs to be said loudly. Giraffe contains a number of fresh, intriguing and fully-achieved poems. It’s well worth seeking out. I well remember reading and being very impressed by Liz Berry’s 2010 Tall Lighthouse debut chapbook, the patron saint of schoolgirls, and this selection from Bryony Littlefair’s early work runs it close. My review of Liz Berry’s subsequent, prize-winning full collection, 

![flowermoonPNG[1]](https://martyncrucefix.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/flowermoonpng1.png?w=437&h=291)
 Frost wants to make big claims for metaphorical thinking: “I have wanted in late years to go further and further in making metaphor the whole of thinking”. He allows the exception of “mathematical thinking” but wants all other knowledge, including “scientific thinking” to be brought within the bounds of metaphor. He suggests the Greeks’ foundational thought about the world, the “All”, was fundamentally metaphorical in nature, especially Pythagoras’ concept of the nature of things as comparable to number: “Number of what? Number of feet, pounds and seconds”. This is the basis for a scientific, empirical (measurable) view of the world and hence “has held and held” in the shape of our still-predominating scientific view of it.
Frost wants to make big claims for metaphorical thinking: “I have wanted in late years to go further and further in making metaphor the whole of thinking”. He allows the exception of “mathematical thinking” but wants all other knowledge, including “scientific thinking” to be brought within the bounds of metaphor. He suggests the Greeks’ foundational thought about the world, the “All”, was fundamentally metaphorical in nature, especially Pythagoras’ concept of the nature of things as comparable to number: “Number of what? Number of feet, pounds and seconds”. This is the basis for a scientific, empirical (measurable) view of the world and hence “has held and held” in the shape of our still-predominating scientific view of it.
 That we have a tendency to forget this provisional nature of knowledge and understanding seems to be Frost’s next point. We take up arms (as it were) by taking up certain metaphorical ideas and making totems of them. He berates Freudianism’s focus on “mental health” as an example of how “the devil can quote Scripture, which simply means that the good words you have lying around the devil can use for his purposes as well as anybody else”. That this is dangerous (makes us not safe) is illustrated by the passage of dialogue Frost now gives between himself and somebody else. The other argues that the universe is like a machine but Frost (adopting a sort of Socratic interrogation technique) draws out the limits of the metaphor, concluding he “wanted to go just that far with that metaphor and no further. And so do we all. All metaphor breaks down somewhere. That is the beauty of it. It is touch and go with the metaphor, and until you have lived with it long enough you don’t know when it is going. You don’t know how much you can get out of it and when it will cease to yield. It is a very living thing. It is as life itself”.
That we have a tendency to forget this provisional nature of knowledge and understanding seems to be Frost’s next point. We take up arms (as it were) by taking up certain metaphorical ideas and making totems of them. He berates Freudianism’s focus on “mental health” as an example of how “the devil can quote Scripture, which simply means that the good words you have lying around the devil can use for his purposes as well as anybody else”. That this is dangerous (makes us not safe) is illustrated by the passage of dialogue Frost now gives between himself and somebody else. The other argues that the universe is like a machine but Frost (adopting a sort of Socratic interrogation technique) draws out the limits of the metaphor, concluding he “wanted to go just that far with that metaphor and no further. And so do we all. All metaphor breaks down somewhere. That is the beauty of it. It is touch and go with the metaphor, and until you have lived with it long enough you don’t know when it is going. You don’t know how much you can get out of it and when it will cease to yield. It is a very living thing. It is as life itself”.




 It may be that this ability to be sustained by scraps and glimpses, the sense that the self is most fully resolved in a lack of egotism, in its encounter with ordinary things, can diminish some of the sting of mortality. In a poem like ‘White’, MacRae manages to celebrate again the ordinariness of familiar things while at the same time sustaining a contentedness (or at least an absence of fear) at the prospect of the self’s vanishing: “You can disappear in a house where / you feel at home; the rooms are spaces / for day-dreams, maps of an interior / turned inside out”. Rather than Macbeth, it is Hamlet’s resolve to “let be” that comes to mind as this calm, accessible, colourful and wonderfully dignified poem concludes:
It may be that this ability to be sustained by scraps and glimpses, the sense that the self is most fully resolved in a lack of egotism, in its encounter with ordinary things, can diminish some of the sting of mortality. In a poem like ‘White’, MacRae manages to celebrate again the ordinariness of familiar things while at the same time sustaining a contentedness (or at least an absence of fear) at the prospect of the self’s vanishing: “You can disappear in a house where / you feel at home; the rooms are spaces / for day-dreams, maps of an interior / turned inside out”. Rather than Macbeth, it is Hamlet’s resolve to “let be” that comes to mind as this calm, accessible, colourful and wonderfully dignified poem concludes: For MacRae’s interest in and skill with poetic form, we need look no further than the extraordinary glose on a quatrain from Alice Oswald (the earlier collection contained another on lines from Mary Oliver). For most poets, this form is little more than an exhibitionist high-wire act, but MacRae’s poems are moving and complete. Her use of poetic form here, particularly in some of these last poems, reminds me of Tony Harrison’s conviction that its containment “is like a life-support system. It means I feel I can go closer to the fire, deeper into the darkness . . . I know I have this rhythm to carry me to the other side” (Tony Harrison: Critical Anthology, ed. Astley, Bloodaxe Books, 1991, p.43). Appropriately, in ‘Jar’, she contemplates with admiration an object that has “gone through fire, / risen from ashes and bone-shards / to float, nameless, into our air”. Here, the narrator movingly lays aside the wary scepticism of the Thomas epigraph and rests her cheek on the jar’s warmth to “feel its gravity-pull / as if it proved the afterlife of things”.
For MacRae’s interest in and skill with poetic form, we need look no further than the extraordinary glose on a quatrain from Alice Oswald (the earlier collection contained another on lines from Mary Oliver). For most poets, this form is little more than an exhibitionist high-wire act, but MacRae’s poems are moving and complete. Her use of poetic form here, particularly in some of these last poems, reminds me of Tony Harrison’s conviction that its containment “is like a life-support system. It means I feel I can go closer to the fire, deeper into the darkness . . . I know I have this rhythm to carry me to the other side” (Tony Harrison: Critical Anthology, ed. Astley, Bloodaxe Books, 1991, p.43). Appropriately, in ‘Jar’, she contemplates with admiration an object that has “gone through fire, / risen from ashes and bone-shards / to float, nameless, into our air”. Here, the narrator movingly lays aside the wary scepticism of the Thomas epigraph and rests her cheek on the jar’s warmth to “feel its gravity-pull / as if it proved the afterlife of things”.









 *As a labouring translator myself, I have long remembered Grigson’s brilliant put-down in his Introduction to the Faber Book of Love Poems (1973). Explaining why he has not included any translations at all, he declares that their “unmeasured, thin-rolled short crust” would prove detrimental to the health of the nation’s poetic taste. Times have changed, thank goodness.
*As a labouring translator myself, I have long remembered Grigson’s brilliant put-down in his Introduction to the Faber Book of Love Poems (1973). Explaining why he has not included any translations at all, he declares that their “unmeasured, thin-rolled short crust” would prove detrimental to the health of the nation’s poetic taste. Times have changed, thank goodness.











 .
.


![1074-Poetry-Review_Cover-RGB-300-w-shadow-429x600[1]](https://martyncrucefix.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/1074-poetry-review_cover-rgb-300-w-shadow-429x6001.jpg?w=199&h=279)
![jellyfish[1]](https://martyncrucefix.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/jellyfish1.jpg?w=700)
![alpine-skiing-877410_640[1]](https://martyncrucefix.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/alpine-skiing-877410_6401.jpg?w=348&h=261)



