During lockdown there has been a proliferation of on-line poetry readings and launches and most of those I have attended have been very successful. I had to teach my (well educated) daughter the meaning of ‘necessity being the mother of invention’ the other day and the poetry world is not the only one learning new ways to do old things. My publisher, Seren Books, has been particularly active in this area, recently staging the launch of Katrina Naomi’s new collection, Wild Persistence and running a mini festival, their Stay-At -Home series. It was during this series of events that I heard Ben Wilkinson read from his 2018 collection, Way More Than Luck. As part of his own reading, Wilkinson also read Louise MacNeice’s ‘Wolves’: “Come then all of you, come closer, form a circle, /Join hands…”
 I’m not proud to admit that Way More Than Luck passed me by when it was first published. As you are probably aware, Wilkinson reviews poetry regularly for The Guardian, and he’s very familiar on social media as a poet and critic, a distance runner and a passionate Liverpool football fan. But the book’s cover (Dalglish, I think), its title and some of the publicity persuaded me that the football bit was going to be predominant. It’s certainly an almost unique aspect of the collection, but it turns out the debilitating darkness of psychological depression is an even more significant one. Wilkinson signals this concern via the book’s two epigraphs. One is about the nature of depression by Matt Haig and a second by John Hanc links challenging physical activities with mental strength, with “state of mind”. And the opening poem immediately suggests the un-put-downable burden of depression for those who struggle with it, while ‘Days’ obsessively lists multiple occasions blighted by it. Both poems use repetition as a device to evoke the persistent nature of depressive episodes, while ‘Pal’ uses that plus personification to convey its haunting, abusive nature:
I’m not proud to admit that Way More Than Luck passed me by when it was first published. As you are probably aware, Wilkinson reviews poetry regularly for The Guardian, and he’s very familiar on social media as a poet and critic, a distance runner and a passionate Liverpool football fan. But the book’s cover (Dalglish, I think), its title and some of the publicity persuaded me that the football bit was going to be predominant. It’s certainly an almost unique aspect of the collection, but it turns out the debilitating darkness of psychological depression is an even more significant one. Wilkinson signals this concern via the book’s two epigraphs. One is about the nature of depression by Matt Haig and a second by John Hanc links challenging physical activities with mental strength, with “state of mind”. And the opening poem immediately suggests the un-put-downable burden of depression for those who struggle with it, while ‘Days’ obsessively lists multiple occasions blighted by it. Both poems use repetition as a device to evoke the persistent nature of depressive episodes, while ‘Pal’ uses that plus personification to convey its haunting, abusive nature:
Next time you’re trying to stand your ground –
argue your case, sprint the home straight,
stare yourself down in the mirror at eight –
he’ll be there alright. His smile is a frown.
His frown is a scowl. His scowl is the fear
you hoped was long gone. Still here. Still here.

Wilkinson’s admiration for MacNeice can be heard in the vigorous syntax here, the use of form and rhyme and his liking for repetition perhaps reflects something of the 1930s poet’s “controlled flamboyance of diction”. Even more successfully, ‘Hound’ treats depression as a beast (an idea famously and perhaps erroneously linked with Winston Churchill):
Know it’s no dog but a phantom,
fur so dark it gives back nothing,
see your hand pass through
its come-and-go presence,
air of self-satisfied deception,
just as the future bursts in on
the present, its big I am, and that
sulking hound goes to ground again.
Troubling dreams feature in two powerful poems. ‘The Nightmare’ is all the more frightening in remaining aware of the real-life episode the dream is based on. A long drive, “to Newby, Lawkland, Cleatop”, is transmuted as the car shudders, the windscreen warps, roadside trees shrivel and the narrator’s companion is suddenly “nowhere to be found”. ‘Stag’ rehearses something similar – the real animal, “on the bypass that night – / antlers like a winter oak”, is, in the dreamed version, pursued vainly across a landscape, seemingly in hope that some secret communication might be recovered from “those cavernous eyes”.

Perhaps the best poem in the book, ‘To David Foster Wallace’, is addressed to the American writer who himself struggled with depression and alcoholism. Wilkinson’s poem takes up a wholly convincing, chatty, MacNeicean tone to discuss – frankly – the experience of despair, “the unpindownable feeling / of hopelessness, hard frustration”. The poem itself declares it takes “courage” to appear weak and it certainly takes courage to write as nakedly as this. Of course, all lyric poetry is to some degree “dramatic”, but there seems a strong autobiographical element to this poem (and others). The poem ends with the narrator explaining that there are occasions, while out running (“my breath dogged on the fellside”), when he experiences something of “peace”, something of psychological relief. Wilkinson’s book title turns out to be not an allusion to a Fernando Torres wonder goal, but what the struggling narrator is left hoping for from David Foster Wallace, even from beyond the grave: “Wish me way more than luck”.
 For me, it’s these psychological truths that Wilkinson is so good at conveying. There are other poems later in the book (and perhaps ‘Stag’ is an elusive example) which begin to sketch episodes of a foundering romantic relationship and ‘Building a Brighter, More Secure Future’ is a very effective excursion into witty political satire (a skilfully handled sestina based on the Conservative Party election manifesto, 2015). And there are the football poems. They comprise the central sequence of 14 poems, introduced with a heart-felt Prologue that says what follows is for the ordinary football fans, written out of “a love beyond the smear campaigns, / the media’s hooligans”. A large part of what Wilkinson has in mind here is the shocking response in parts of the media to the Hillsborough tragedy in 1989, when 96 men, women and children died (David Cain’s Forward prize shortlisted book, Truth Street, from Smokestack Books, movingly dealt with this event and the media and policing responses and I reviewed it last summer). Wilkinson obliquely refers to the occasion in ‘Kenny Dalglish’ and several poems have worthwhile things to say about racism in the game (‘John Barnes’) and how the game can offer an escape route for working class boys (‘Billy Liddell’ and ‘Steven Gerrard’).
For me, it’s these psychological truths that Wilkinson is so good at conveying. There are other poems later in the book (and perhaps ‘Stag’ is an elusive example) which begin to sketch episodes of a foundering romantic relationship and ‘Building a Brighter, More Secure Future’ is a very effective excursion into witty political satire (a skilfully handled sestina based on the Conservative Party election manifesto, 2015). And there are the football poems. They comprise the central sequence of 14 poems, introduced with a heart-felt Prologue that says what follows is for the ordinary football fans, written out of “a love beyond the smear campaigns, / the media’s hooligans”. A large part of what Wilkinson has in mind here is the shocking response in parts of the media to the Hillsborough tragedy in 1989, when 96 men, women and children died (David Cain’s Forward prize shortlisted book, Truth Street, from Smokestack Books, movingly dealt with this event and the media and policing responses and I reviewed it last summer). Wilkinson obliquely refers to the occasion in ‘Kenny Dalglish’ and several poems have worthwhile things to say about racism in the game (‘John Barnes’) and how the game can offer an escape route for working class boys (‘Billy Liddell’ and ‘Steven Gerrard’).
 But the poems also show how difficult it is to escape the miasma of cliché that seems to engulf football itself. Anfield is filled with a “fabled buzz”, then “the place erupt[s]”. Barnes unleashes a “a sweeping, goal-bound ball”, and a particular game offers one “last-ditch twist”. I’m reminded of Louis MacNeice’s observation (now sadly compromised in various ways, but the spirit of it remains valid, I think) that he wanted a poet not to be “too esoteric. I would have a poet able-bodied [sic], fond of talking, a reader of the newspapers, capable of pity and laughter, informed in economics, appreciative of women [sic], involved in personal relationships, actively interested in politics, susceptible to physical impressions’. There are many more of these poets around these days and to bring (even) football into the purview of poetry can hardly be a bad thing. Yet it is not an easy one and there may be some risks in deciding to headline the attempt. Ian Duhig’s blurb note to Way More Than Luck has gingerly to negotiate this issue: “The beautiful game inspires some beautiful poems in Ben Wilkinson’s terrific debut collection … but there’s far more than football to focus on here”. Yes, indeed.
But the poems also show how difficult it is to escape the miasma of cliché that seems to engulf football itself. Anfield is filled with a “fabled buzz”, then “the place erupt[s]”. Barnes unleashes a “a sweeping, goal-bound ball”, and a particular game offers one “last-ditch twist”. I’m reminded of Louis MacNeice’s observation (now sadly compromised in various ways, but the spirit of it remains valid, I think) that he wanted a poet not to be “too esoteric. I would have a poet able-bodied [sic], fond of talking, a reader of the newspapers, capable of pity and laughter, informed in economics, appreciative of women [sic], involved in personal relationships, actively interested in politics, susceptible to physical impressions’. There are many more of these poets around these days and to bring (even) football into the purview of poetry can hardly be a bad thing. Yet it is not an easy one and there may be some risks in deciding to headline the attempt. Ian Duhig’s blurb note to Way More Than Luck has gingerly to negotiate this issue: “The beautiful game inspires some beautiful poems in Ben Wilkinson’s terrific debut collection … but there’s far more than football to focus on here”. Yes, indeed.
 I am very grateful to Ian Brinton’s and Michael Grant’s recent translation of a selected Mallarmé (Muscaliet, 2019) for sending me back to a poet who has always proved problematic for me. My natural inclination draws me more to Louis MacNeice’s sense of the “drunkenness of things being various” (‘Snow’) – his emphasis on poetry’s engagement with “things” – and his desire to communicate pretty directly with his fellow wo/man, than with what Elizabeth McCombie bluntly calls “the exceptional difficulty” of Mallarmé’s work. I appreciate that such a dichotomy seems to shove the French poet into an ivory tower (albeit of glittering and sensuous language) while casting the Irish one as too narrowly engagé, but I’m also aware that Sartre praised Mallarmé as a “committed” writer and that, despite some evident remoteness from the ‘tribe’, the French poet’s political views were both radical and democratic.
I am very grateful to Ian Brinton’s and Michael Grant’s recent translation of a selected Mallarmé (Muscaliet, 2019) for sending me back to a poet who has always proved problematic for me. My natural inclination draws me more to Louis MacNeice’s sense of the “drunkenness of things being various” (‘Snow’) – his emphasis on poetry’s engagement with “things” – and his desire to communicate pretty directly with his fellow wo/man, than with what Elizabeth McCombie bluntly calls “the exceptional difficulty” of Mallarmé’s work. I appreciate that such a dichotomy seems to shove the French poet into an ivory tower (albeit of glittering and sensuous language) while casting the Irish one as too narrowly engagé, but I’m also aware that Sartre praised Mallarmé as a “committed” writer and that, despite some evident remoteness from the ‘tribe’, the French poet’s political views were both radical and democratic. So, if we must give up on such ‘understanding’, what was Mallarmé – writing in the 1880-90s – doing? Something recognisably very modern, it turns out. Contra Wordsworth (and MacNeice, I guess), Mallarmé and his Symbolist peers, held ordinary language in suspicious contempt as too ‘journalistic’, too wedded to a world of facts. Poetry was to be more a communication, or evocation, of emotion, of a detachment from the (merely) everyday and a recovery of the mystery of existence which rote and routine has served to bury. Such a role demanded linguistic innovation as suggested in ‘The Tomb of Edgar Poe’ in which the American writer is praised for giving “purer meaning to the words of the tribe” (tr. Brinton/Grant). Writing about Edouard Manet’s work, Mallarmé saw the need to “loose the restraint of education” which – in linguistic terms – would mean freeing language from its contingent relations to the facticity of things (and the tedium and ennui that results from our long confinement to them) and hence moving language nearer to what he called the “Idea” and the paradoxical term Nothingness (as Brinton/Grant translate “le Neant”).
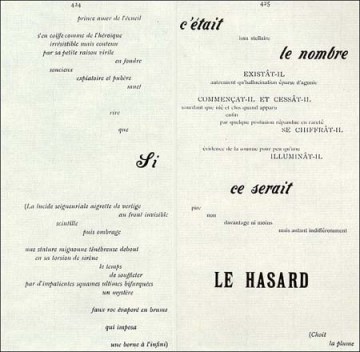
So, if we must give up on such ‘understanding’, what was Mallarmé – writing in the 1880-90s – doing? Something recognisably very modern, it turns out. Contra Wordsworth (and MacNeice, I guess), Mallarmé and his Symbolist peers, held ordinary language in suspicious contempt as too ‘journalistic’, too wedded to a world of facts. Poetry was to be more a communication, or evocation, of emotion, of a detachment from the (merely) everyday and a recovery of the mystery of existence which rote and routine has served to bury. Such a role demanded linguistic innovation as suggested in ‘The Tomb of Edgar Poe’ in which the American writer is praised for giving “purer meaning to the words of the tribe” (tr. Brinton/Grant). Writing about Edouard Manet’s work, Mallarmé saw the need to “loose the restraint of education” which – in linguistic terms – would mean freeing language from its contingent relations to the facticity of things (and the tedium and ennui that results from our long confinement to them) and hence moving language nearer to what he called the “Idea” and the paradoxical term Nothingness (as Brinton/Grant translate “le Neant”). For these reasons, Mallarmé “cede[s] the initiative to words” (‘Crise de Vers’), to language’s material aspects as much as to its referential functions. Carrying over the material aspects of his French verse into English is then, to say the least, difficult. I’m inclined to agree with Weinfield (Introduction to Stephane Mallarmé Collected Poems (Uni. Of California Press, 1994) that it is “essential to work in rhyme and metre, regardless of the semantic accommodations and technical problems this entail[s]. If we take rhyme from Mallarmé, we take away the poetry”. But is that even possible? The accommodations and problems that arise are huge! Mallarmé placed the sonnet, ‘Salut’, at the start of his Poésies as a toast, salutation and mission statement. Weinfield gives the sestet as follows:
For these reasons, Mallarmé “cede[s] the initiative to words” (‘Crise de Vers’), to language’s material aspects as much as to its referential functions. Carrying over the material aspects of his French verse into English is then, to say the least, difficult. I’m inclined to agree with Weinfield (Introduction to Stephane Mallarmé Collected Poems (Uni. Of California Press, 1994) that it is “essential to work in rhyme and metre, regardless of the semantic accommodations and technical problems this entail[s]. If we take rhyme from Mallarmé, we take away the poetry”. But is that even possible? The accommodations and problems that arise are huge! Mallarmé placed the sonnet, ‘Salut’, at the start of his Poésies as a toast, salutation and mission statement. Weinfield gives the sestet as follows:
 Displaying his characteristic flair, craft and intelligence, Crucefix’s poems often begin with the visible, the tangible, the ordinary, yet through each act of attentiveness and the delicate fluidity of the language they re-discover the extraordinary in the everyday.
Displaying his characteristic flair, craft and intelligence, Crucefix’s poems often begin with the visible, the tangible, the ordinary, yet through each act of attentiveness and the delicate fluidity of the language they re-discover the extraordinary in the everyday.





 I
I In lieu of a new blog post, here is a link to the Hercules Editions webpage on which I have formulated a few thoughts about the current lockdown, photography and the (forgotten?) refugee crisis in the Mediterranean. It is a piece in part related to the Hercules publication of my longer poem,
In lieu of a new blog post, here is a link to the Hercules Editions webpage on which I have formulated a few thoughts about the current lockdown, photography and the (forgotten?) refugee crisis in the Mediterranean. It is a piece in part related to the Hercules publication of my longer poem, 


 This is Walford Davies’ fourth book from Seren and it is an ambitious project, combining narrative and lyric form (every poem is 16 lines long, in unrhymed couplets, most in four beat lines). It’s also a dramatic monologue, in effect, as the speaker is a thoroughly unpleasant, arrogant, but haunted architect engaged in several large urban projects in Cardiff between the years 1890 and 1982. Talk about the male gaze, this man epitomizes it. He and his wife have recently buried a child lost in stillbirth (“they wrapped it in a pall // not bigger than my handkerchief”) and while she mourns the loss, he gets on with his work and frequents bars and prostitutes in Cardiff’s docklands. The sympathetic reader is probably going to try to read this man’s cruel and dismissive treatment of his wife (and his exploitative relationships with other women) as his own rather twisted way of dealing with grief. But it’s hard to maintain that view, as Walford Davies is often shockingly good at catching his loathsome attitudes, especially towards women: “This quarter grows on me. / In shabby rooms in Stuart Street // my new friend swears // she’ll tackle anything for oranges”.
This is Walford Davies’ fourth book from Seren and it is an ambitious project, combining narrative and lyric form (every poem is 16 lines long, in unrhymed couplets, most in four beat lines). It’s also a dramatic monologue, in effect, as the speaker is a thoroughly unpleasant, arrogant, but haunted architect engaged in several large urban projects in Cardiff between the years 1890 and 1982. Talk about the male gaze, this man epitomizes it. He and his wife have recently buried a child lost in stillbirth (“they wrapped it in a pall // not bigger than my handkerchief”) and while she mourns the loss, he gets on with his work and frequents bars and prostitutes in Cardiff’s docklands. The sympathetic reader is probably going to try to read this man’s cruel and dismissive treatment of his wife (and his exploitative relationships with other women) as his own rather twisted way of dealing with grief. But it’s hard to maintain that view, as Walford Davies is often shockingly good at catching his loathsome attitudes, especially towards women: “This quarter grows on me. / In shabby rooms in Stuart Street // my new friend swears // she’ll tackle anything for oranges”. Walford Davies, in an end note, talks of the ambiguity of the female figures – wife, prostitutes, dead girl – who do tend to float without clear identity, disembodied, through the text. It adds something to the ghost-like quality of the book, but the loss is any more powerful evocation of them. Also, the choice of brief lyrics to develop what could well have been a novel, gives the reader some powerful moments but few prolonged engagements with any of the characters. And the nature of the central male figure is problematic because of his downright unpleasantness (though, I suppose, Browning managed it in ‘My Last Duchess’) and in 2020 there will be plenty of readers who find such a portrayal an absolute bar to reading. I don’t think Walford Davies ironises and critiques his male figure enough, or clearly enough.
Walford Davies, in an end note, talks of the ambiguity of the female figures – wife, prostitutes, dead girl – who do tend to float without clear identity, disembodied, through the text. It adds something to the ghost-like quality of the book, but the loss is any more powerful evocation of them. Also, the choice of brief lyrics to develop what could well have been a novel, gives the reader some powerful moments but few prolonged engagements with any of the characters. And the nature of the central male figure is problematic because of his downright unpleasantness (though, I suppose, Browning managed it in ‘My Last Duchess’) and in 2020 there will be plenty of readers who find such a portrayal an absolute bar to reading. I don’t think Walford Davies ironises and critiques his male figure enough, or clearly enough.