Genuinely acclaimed first books can be hard to follow up. Raymond Antrobus’ The Perseverance (Penned in the Margins, 2018) was a Poetry Book Society Choice and won the Ted Hughes Award and the Rathbone’s Folio Prize in 2019. I reviewed the book that year as one of the five collections shortlisted for the Forward Felix Dennis First Collection Prize. In many ways it was a conventional book of poems – its voice was colloquial, it successfully employed a range of (now) traditional forms (dramatic monologues, prose poem, sestina, ghazal, pantoum), its syntax and punctuation were nothing out of the ordinary. Its subject matter was to a large extent dominated by a son’s difficult relationship with his father, by questions of racial identity and (this is what made it especially distinctive) the experience of a young Deaf man. Besides the latter, what really marked the book out (I argued) was ‘that impossible-to-teach, impossible-to-fake, not especially ultra-modern quality of compassion’. Listen to Raymond Antrobus talking about his first collection here.
Now several years on and literary acclaim, a new publisher (this book is published by Picador Poetry – Penned in the Margins has since sadly ceased operations), a recent marriage and a broadening of perspective (particularly towards the USA) all place Antrobus in a very different environment. He has set aside a lot of the experimentation with recognised forms (which is not to say the new poems do not experiment with poetic form) and the book opens very positively:
Give thanks to the wheels touching tarmac at JFK,
give thanks to the latches, handles, what we squeeze
x
into cabins, the wobbling wings, the arrivals,
departures, the long line at the gates, the nerves held,
x
give thanks to the hand returning the passport [. . .]
In a similar tone, ‘The Acceptance’ concludes with the word ‘Welcome’ being signed. But the 30 lines preceding this hark back to that ‘complicated man’ (a phrase from ‘Dementia’, from The Perseverance), the poet’s father. Though dead for several years now, he continues to haunt his son’s dreams and a number of these new poems. In ‘Every Black Man’, the ‘dark dreadlocked Jamaican father’ meets his prospective, English mother-in-law for the first time. He’s already drunk, there is shouting, he lashes out, she racially insults him: they never meet in the same room again. The father’s ‘heartless sense of humour’ is turned into a slow blues: ‘I think that’s how he handled pain, drink his only tutor’ (‘Heartless Humour Blues’). And the man’s ‘complication’ is reaffirmed in the poem, ‘Arose’, in which, talking to his embarrassed son, the father boasts of the great sex had with the boy’s mother, but then is touchingly remembered, calling out her name: ‘Rose? And he said it like something in him / grew towards the light.’
But All The Names Given also pays more fulsome tribute to Antrobus’ mother. In ‘Her Taste’, despite her conventional, English, religious background, she drops out, joins a circus (literally, I think!), has various relationships, and eventually gets pregnant by Seymour, the ‘complicated man’ from Jamaica, who left her to raise the children. Thirty years on, she’s defiant, independent, ‘holding her head higher at seventy’. We see her leafing through a scrapbook of her past, ‘rolling a spliff on somebody’s balcony’ or again, ‘in church reading Bertrand Russell’s ‘Why I’m Not a Christian’.’ Despite such moments, the maternal portrait does not quite possess the vivid distinctiveness of the paternal one. But, with the benefit of the passing years, Antrobus can now write, ‘On Being A Son’, in which he unreservedly praises Rose in her neediness, her self-sufficiency, her helplessness with IT, her helpfulness in so much else. He concludes, channelling her voice: ‘mother / dyes her hair, / don’t say greying / say sea salt / and cream’.
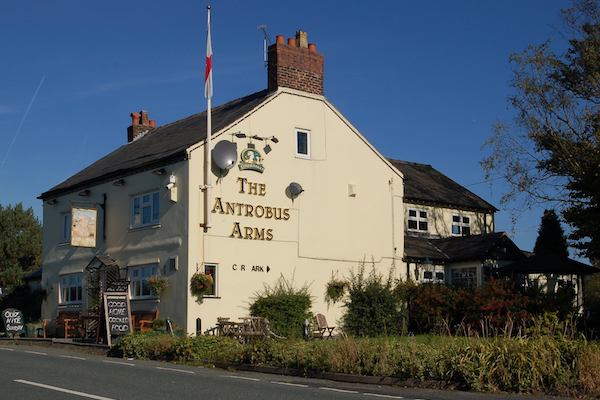
This greater focus on the mother is partly a redressing of the previous book’s gender imbalance, but it is also at one with Antrobus’ interest in family and heritage as offering clues to his own identity. It turns out the Antrobus name – from his mother’s English side – is anciently English (or far distantly Norse) and associated with Antrobus in Cheshire. ‘Antrobus or Land of Angels’ records a visit (by mother and son) to the place, to face the suspicious looks in The Antrobus Arms, the guard dogs at the Hall:
A farmer appears, asks if we’re descended
from Edmund Antrobus.
x
Sir Edmund Antrobus, (3rd baronet)
slaver, beloved father,
over-seer, owner of plantations
x
in Jamaica, British Guiana and St Kitts.
The son’s quick denial of the line of descent is a complex moment. Despite carrying the same name, his mother is not truly a descendant. But given His Lordship’s slave-owning history, who is to say whether there is any genetic relation, ironically, through his Jamaican-born father, Seymour. The thought surfaces in ‘Horror Scene as Black English Royal (Captioned)’. Antrobus’ note tells us this poem was sparked by tabloid/CNN speculations in 2019 about the likely ‘blackness’ of the Sussexes’ royal baby. The poem’s narrator looks down at his own hands and sees ‘your great-great-great Grandfather’s owner’s hands’.
So All The Names Given quickly reveals itself to be a book deeply troubled by the kinds of questions raised in the poem ‘Plantation Paint’: ‘Why am I like this? // What am I like? / Who does / it matter to?’ In this second book, Antrobus is still working towards an ‘overstanding’. The idea was alluded to in The Perseverance via a Peter Tosh lyric: ‘love is the man overstanding’. It is a form of understanding that emerges after all untruths have been overcome. The truths, untruths and complications of identity preoccupy the majority of these new poems. Only occasionally does Antrobus set aside such profound (perhaps irresolvable) anxieties. The African/Vietnamese waitress in ‘A Short Speech Written on Receipts’ is a figure who seems to outweigh the poet’s wrangling over his own selfhood, leading him to wonder: ‘Maybe kindness is how / you take down the stalls’. The gates of compassion also open frankly and to great effect in ‘At Every Edge’ and ‘A Paper Shrine’, two brief poems remembering very different students in creative writing classes. Likewise, ‘For Tyrone Givans’, commemorates a young Deaf man (a friend and contemporary of Antrobus) who committed suicide in Pentonville Prison in 2018. Here too, the vector of attention is outwards, towards Tyrone’s mistreatment by the authorities, his suffering and despair, rather than inwards towards the poet’s own ‘complications’:
Tyrone, the last time I saw you alive
I’d dropped my pen
on the staircase
x
didn’t hear it fall but you saw and ran
down to get it, handed it to me
before disappearing, said,
x
you might need this.
This review was originally commisioned and published by The High Window